The Twelve Factor App
12factor.net - Link
Introduction
Methodology for building software-as-a-service app that:
- Use Declarative formats for setup automation, to minimize time and cost for new developers joining the project.
- Have a Clean Contract with the underlying operation system, offering Maximum Portability between execution environments
- Are suitable for Deployment on modern Cloud platforms, obviating the need for servers and system administrators
- Minimize divergence between deployment and production, enabling Continuous deployment for maximum agility
- And can Scale up without significant changes to tooling, architecture, or development practices.
The Twelve Factors
1. Codebase
One codebase tracked in revision control, many deploys
- Multiple apps sharing the same code is a violation of twelve-factor. The solution here is to factor shared code into libraries which can be included through the dependency manager
2. Dependencies
Explicity declare and isolate dependencies
- A twelve-factor app never relies on implicit existence of system-wide packages.
- It declares all dependencies, completely and exactly via a dependency declaration manifest
- It uses dependency isolation tool during execution to ensure that no implicit dependency specification is applied uniformly to both production and development
- Another benefits of explicitly declaring dependency is that it allows new developers to quickly run application locally.
3. Config
Store Config in the environment
- Apps storing config as constants in the code is violation of twelve-factor, which requires strict separation of config from code.
4. Backing Services
Treat backing services as attached resources
- A backing service is any service that app consumes over the network as part of its normal operation. Eg, Datastore (MySQL, MongoDB), Messaging (RabbitMQ), SMTP Services and Caching System
- The code for twelve-factor app makes no distinction between local and third party services. To the app, both are attached resources, accessed via a URL or other locator/credentials stored in the config
- Each distinct backing service is a resource. The twelve-factor app treats these databases as attached resources, which indicate their loose coupling to the deploy they are attached to.
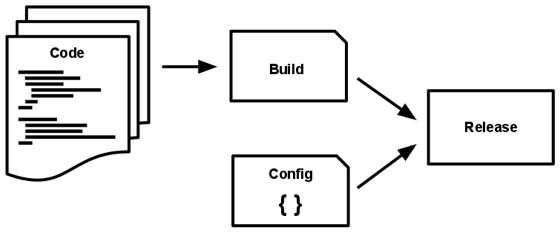
5. Build, Release, Run
Strictly separate build and run stages
- The Build Stage is a tranform which converts a code repo into an executable bundle known as build. Using a version of the code at a commit specified by the development process, the build stage fetches vendors dependencies and compiles binaries and assets
- The Release Stage takes the build produced by the build stage and combines it with the deploy’s current config. The resulting relrease contains both the build and the config and is ready for immediate execution in the execution environment.
- The Run Stage runs the application in the execution environment, by launching some set of the app’s process against a selected release.
- Every release should always have a unique release ID
- Release cannot be mutated once its created. Any change must create a new release
6. Processes
Execute the app as one or more stateless Processes
- Twelve-factor process are stateless and share-nothing
- Sticy sessions are a violation of twelve-factor; Session state data is a good candidate for a datastore that offers time-expiration, such as Memcached
7. Port Binding
Export services via port Binding
- The twelve-factor app is completely self-contained and does not rely on runtime injection of a webserver into the execution environment to create a web-facing services. The web app exports HTTP as a service by binding to a port, and listening to requests coming in on that port.
- Note also that the port-binding approach means that one app can become the backing service for another app, by providing the URL to the backing app as a resource handle in the config for the consuming app.
8. Concurrency
Scale out via the process model
- In the twelve-factor app, processess are a first class citizen.
- The process model truly shines when it comes time to scale out. The share-nothing, horizontal partionable nature of twelve-factor app process means that adding more concurrency is a simple and reliable operation.
9. Disposability
Maximize robustness with fast startup and graceful shutdown
- The twelve-factor app’s processess are disposable, meaning they can be started or stopped at a moment’s notice.
10. Dev / Prod Parity
Keep development, staging and production as similar as possible
- The twelve-factor app is designed for continuous deployment by keeping the gap between development and production small.
- The twelve-factor developers resists the urge to use different backing services between development and production, even when adapters theoritically abstract away differences in backing services.
11. Logs
Treat logs as event streams
- Twelve-factor app never concerns itself with routing or storage of its output stream
- It should not attempt to write to or manage logfiles, instead each running process writes its event stream, unbuffered, to
stout
12. Admin Process
Run admin / management tasks as one-off processes
- Twelve-factor strongly favors languages which provide a REPL shell out of the box, and which make it easy to run one-off scripts. In a local deploy, developers invoke one-off admin processes by a direct shell command inside the app’s checkout directory. In a production deploy, developers can use ssh or other remote command execution mechanism provided by that deploy’s execution environment to run such a process.