01 - Architecture 101
- Access Management Basics
- Shared Reponsibility Model
- Service Models
- Availability and Fault Tolerance
- Scalling
- Tiered Application Design
- Encryption
Access Management Basics
Principal - A person or application that can make an authenticated or anonymous request to perform an action on a system.
Authentication - The process of authenticating a principal against an identity. This could be via username and passsword or API Keys.
Identity - Objects that require authentication and are authorized to access resources.
Authorization - The process of checking and allowing or denying access to a resoruce for an identity.
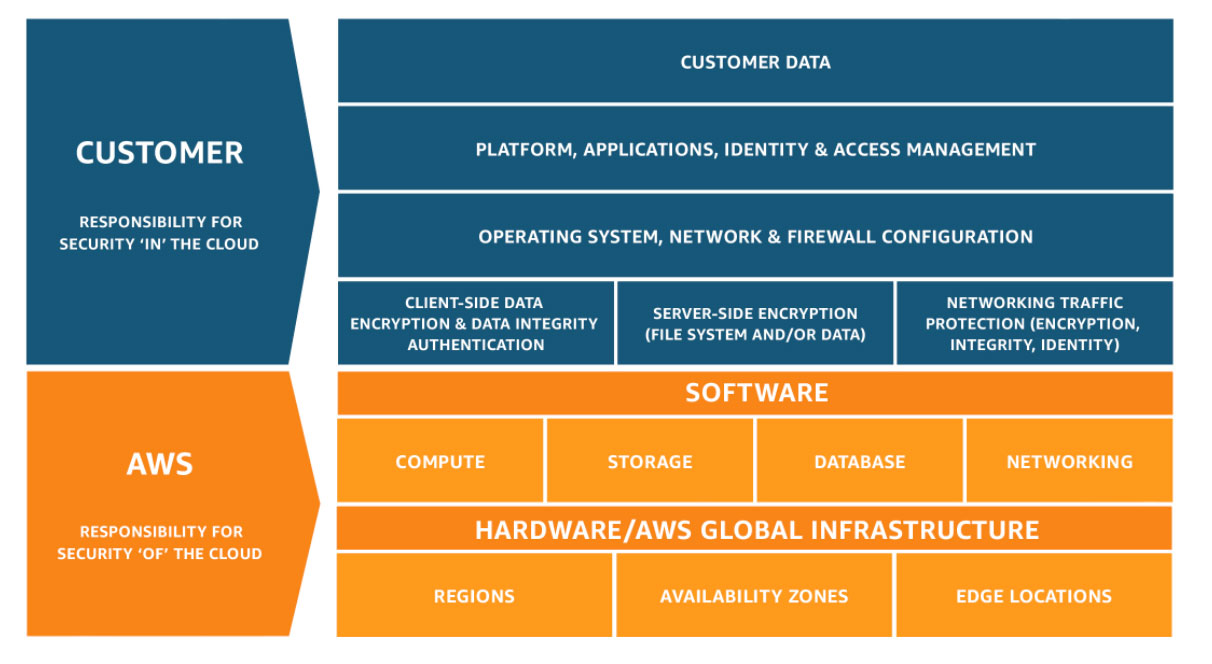
Shared Reponsibility Model
-
AWS is responsible for the “Security of the Cloud”, This infrastructure is composed of the hardware, software, networking, and facilities that run AWS Cloud services.
-
Customer is responsible for the “Security in the Cloud”, Customers are responsible for managing their data (including encryption options), classifying their assets, and using IAM tools to apply the appropriate permissions.
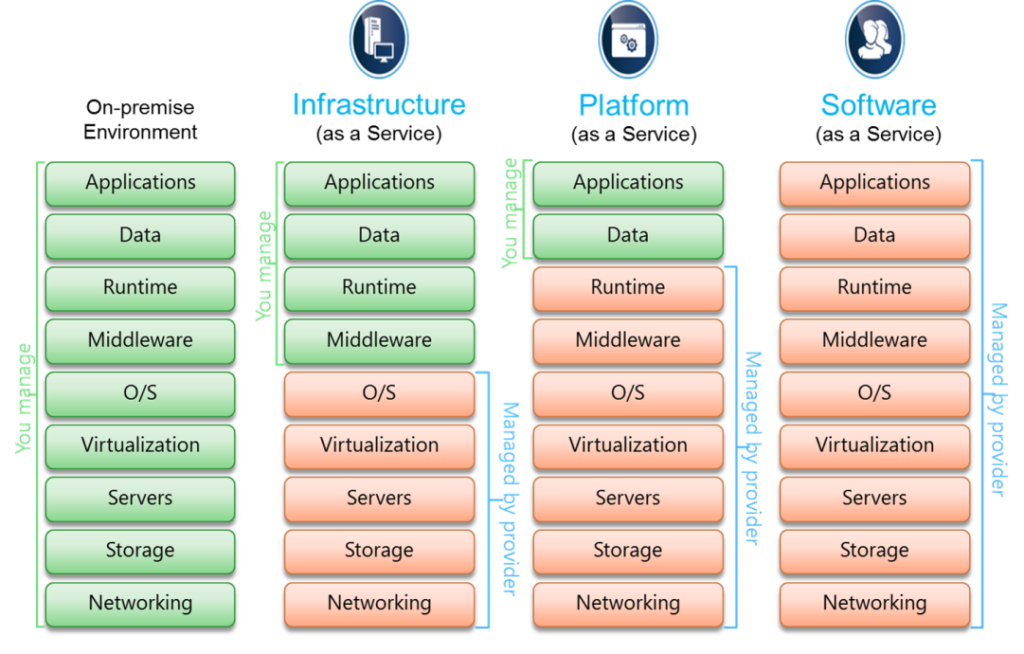
Service Models
Service models define how a service or product is delivered, How you pay and what you receive. They also define which part of the product you manage and accept the risk for, as well as which part the vendor is responsible for.
Cloud models come in three types: SaaS (Software as a Service), IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service). Each of the cloud models has their own set of benefits that could serve the needs of various businesses.
Availability and Fault Tolerance
High Availability - Hardware, Software and configuration allowing a system to recover quickly in the event of a failure.
Fault Tolerance - System designed to operate though a failure with no use impact. Fault Tolenace is more expensive and complex to achieve.
Recory Point Objective (RPO) - How much a business can tolerate to lose, expressed in time. The maximum time between a failure and the last successful backup.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) - The maximum amount of time a system can be down. How long a solution takes to recover.
Scalling
-
Vertial Scalling (Down/Up) is achieved by adding additional resources in from of CPU or memory to existing machine. By doing so, the machine is able to service additional customers or perform compute tasks quicker. Eventually, maximum machine size will constraint your ability to scale - either technically or from a cost perspective.
-
Horizontal Scalling(Right/Left) is achieved by adding additional machines into a pool of resource, each of which provide the same service. Horizontal scalling suffers none of the size limitations of vertical scalling and can scale to nearly infinite levels but requires application support to scale effectively.
Tiered Application Design
Architectually, applications consist of three tiers: Presentation Tier, which intereacts with the customer of the application, the logic tier, which delivers the application functionality; and the data tier, which controls interaction with a database.
Encryption
Encryption is the process of taking plaintext and converting it into ciphertext, and converting ciphertext into plaintext. Plaintext and cipheredtext can be text, images or other data.
Types of Enryption
- Symmetrical - Same key is used for both encryption and decryption
- Asymmetrical - Different keys - called public and private keys are used
- Cost efficient or Cost Effective