04 (A) - Compute Services - Server Based
- Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2)
- Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
- EBS Snapshots
- Security Groups
- Instance Metadata
- AMI
- Bootstrap
- Private Instance and Public Instance
- Advanced Topics
Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2)
EC2 is one of the most widely used services within AWS. As an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) product, it’s responsible for providing long-running compute as a service.
EC2 instances are grouped into families, which are designed for a specific broad type workload. The type determines a certain set of features, and size decide the level of workload they can cope with.
The current EC2 families are:
- General Purpose
- Compute Optimized
- Memory Optimized
- Storage Optimized
- Accelerated Computing
Instance Types include:
- T2 and T3: Low cost instance types that provide burst capability
- M5: for general Workoads
- C4: Provides more capable CPU
- X1 and R4: Optimize large amounts of Fast Memory
- I3: Delivers fast IO
- P2, G3 and F1: Deliver GPU and FPGA
Instance sizes include Nano, Small, Medium, Large, X.Large, 2X.Large and Larger
Special Cases
- “a”: Use AMD CPU
- “A”: Arm based
- “n”: Higher speed networking
- “d”: NVMe storage
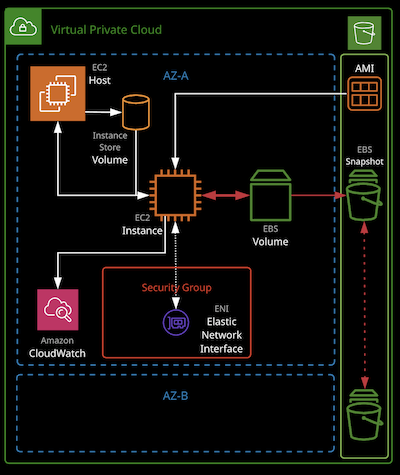
Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
Elastic Block Storage is a storage service that creates and manages volumes based on four underlying storage types. Volumes are persistent, can be attached and removed from EC2 instances, and are replicated within a single AZ.
Info
To protect against AZ failure, EBS snapshots (to S3) can be used. Data is replicated across AZs in the region and (optionally) internationally.
Exam Facts
- EBS supports a maximum per-instance throughput of 1750 MiB/s and 80,000 IOPS.
General Purpose (gp2): (SSD)
- Default for most workloads
- 3 IOPS/GB (100 IOPS - 16,000 IOPS)
- Burst up to 3,000 IOPS (credit based)
- Volume Size of 1 GiB - 16 TB size, max throughput p/vol of 250 MB/s
Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1): (SSD)
- Used for application that require sustained IOPS performance
- Large database workloads
- Volume size of 4 GB - 16TB, max throughput of 1000 MB/s
Throughput Optimized(st1): (HHD)
- Low storage cost
- Used for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads (streaming, bigdata)
- Cannot be a boot volume
- Volume size of 500GB - 16TB
- Max throughput - 500MB/s and IOPS 500
Cold HDD (sc1): HDD
- Lowest cost
- Infrequent accessed data
- Cannot bee a boot volume
- Volume size of 500 GB - 16 TB
- Max throughput - 250MB/s and IOPS 250
EBS Snapshots
EBS Snapshots are a point-in-time backup of an EBS volume stored in S3. The initial snapshot is a full copy of the volume. Future snapshots only store the data changed since the last snapshot.
Snapshots can be used to create new volumes and are a great way to move or copy instances between AZs. When creating a snapshot of the root/boot volume of an instance of busy volume, it’s recommended the instance is powered off, or disks are “flushed”
Snapshots can be copied between regions, shared and automated using Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM).
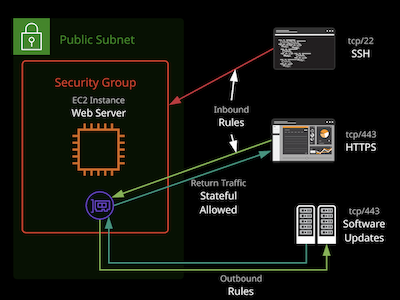
Security Groups
Security Groups are software firewalls that can be attached to network interface and (by association) products in AWS. Security groups each have inbound rules and outbound rules. A rule allows traffic to and from a source (IP, network, named AWS entity) and protocol. Security Group belongs to a VPC
Note
Each Elastic Network Interface (ENI) can have upto 5 security groups.
Info
Security group have a hidden implicit/default deny rule but cannot explicitly deny traffic.
They are stateful - meaning for any traffic allowed in/out, the return traffic is automatically allowed. Security groups can reference AWS resource, other security groups, and even themselves.
Instance Metadata
Instance metadata can be used to access information about an instance from the instance. It allows applications running within EC2 to have visibility into their environment. Instance metadata is data relating to the instance that can be accessed from within the instance itself using a utility capable of accessing HTTP and using the URL
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-dataInstance metadata is a way that scripts and application running on EC2 can get visibility of data they would normally need API calls for.
The metadata can provide the current external IPv4 address for the instance, which isn’t configured on the instance itself but provided by the internet gateway in the VPC. It provides the Availability Zone the instance was lanched in and the security group applied to the instance. IN the case of spot instances, it also provides the approximate time the instance will terminate.
Tip
Remember the IP address to access metadata: 169.254.169.254
AMI
AMIs (Amazon Machine Images) are used to build instance. They store snapshots of EBS volumes, permissions, and a block device mapping, which configures how the instance OS see the attached volumes. AMIs can be shared, free or paid and can be copied to other AWS regions.
Types of AMIs
- Instance Store Back AMIs - Root volume doesn’t use EBS
- EBS Backed AMIs - Root volume uses EBS
Process of Creating AMI
-
Configure Instance - Source instance and attached EBS volumes are configured with any required software and configuration.
-
Create Image - Snapshots are created from volumes. AMI references snapshots, permission, and block device mapping.
-
Launch Instance - With approriate launch permissions, instances can be created from an AMI. EBS volumes are created using snapshots as the source, and an EC2 instance is created uinsg the block device mapping to reference its new volumes.
AMI’s can be used to build servers with complex configuration.
Warning
Downside of using AMI is you can’t do dynamic configuration
Bootstrap
Bootstrapping is a process where instructions are executed on an instance during its launch process. Bootstraping is used to configure the instance, perform software installation, and add application configuraiton.
In EC2, user data can be used to run shell scripts or run cloud-init directives.
Bootstrap vs AMI: With AMI’s you can reduce time it takes to install and configure versus with bootstrap you can use shell commands to perform dynamic configuration.
Private Instance and Public Instance
- Private Instance - Private IP allocated when launching instances. Unchanged during stop/start. Released when terminated.
- Public Instance - Same private address as private instance. A public IPv4 address is allocated when the machine starts and deallocated when it stops. By default all public IPv4 addresses are dynamic
- Elastic IP - Elastic IPs are static. When allocated, they replace the normal public IP, which is deallocated.
Advanced Topics
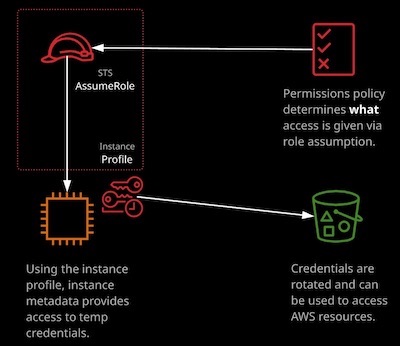
EC2 Instance Roles
EC2 instance roles are IAM roles that can be “assumed” by EC2 using an itermediary called an instance profile. An instance profile is either created automatically when using the console UI or manually when using the CLI. It’s a container for the role that is associated with an EC2 instance.
The instance profile allows application on the EC2 instance to access the credentials from the role using the instance metadata.
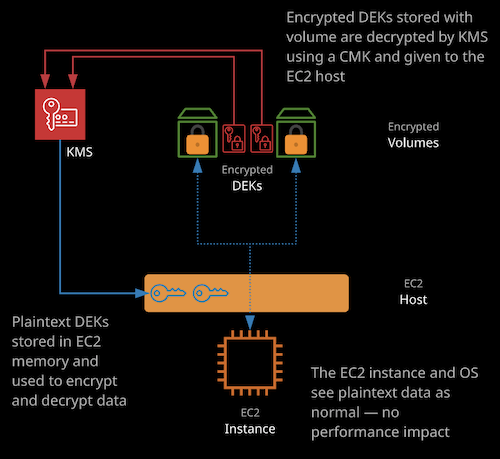
EBS Volume and Snapshot Encryption
Volume encryption uses EC2 host hardware to encrypt data at rest and in transit between EBS and EC2 instances. Encryption generates a data encryption key (DEK) from a customer master key (CMK) in each region. A unique DEK encrypts each volume. Snapshots of that volume are encrypted with the same DEK, as are any volumes created from that snapshot.Encrypted DEKs stored with volume are decrypted by KMS using a CMK and given to the EC2 host.
Plaintext DEKs stored in EC2 memory and used to encrypt and decrypt data. The EC2 instance and OS see plaintext data as normal - no performance impact.
EBS encryption are configured at per volume basis but can also be specified on per-account basis.
Info
If you need to manage the Keys and you need encryption on OS Level, EBS encryption won’t fullfill the need, you would need OS level encryption.
EBS Optimized, Enhanced Networking, and Placement Group
EBS optimization
EBS-optimized mode, which was historically optional is now the default, adds optimizations and dedicated communcation paths for storage and traditional data networking. This allows consistent utilization of both - and is one required feature to support higher performance storage.
Restoring from EBS Snapshot - Not all data is copied immediately to the new volume. Data will be copied over time in the background. This preliminary action takes time and can cause a significant increase in the latency of I/O operations the first time each block is accessed which will temporarily adversely affect performance. Volume maximum performance is achieved after all blocks have been downloaded and written to the volume.
Enhanced networking
Traditionally, virtual networking meant a virtual host (EC2 host) arranging access for n virtual machines to access one physical network card - this multitasking is done in software and is typically slow.
Enhanced networking uses SR-IOV, which allows a single physical network card to appear as multiple physical devices. Each instance can be given one of these (fake) physical devices. This results in faster transfer rate, lower CPU usage, and lower consistent latency. EC2 delivers this via the Elastic Network Adapter (ENA) or Intel 82599 Virtual Function (VF) interface.
Cluster, partition, and spread placement groups
- Cluster Placement Group Cluster placement groups place instances physically near each other in a single AZ. Every instance can talk to each other instance at the same time at full speed. Works with enhanced networking for peak performance.
Info
Use Cluster Placement Group for maximum performance
- Partition Placement Group Instances deployed into a partition placement group (PPG) are separated into partitions, each occupying isolated rack in AZs. PPG can span multiple AZs in a region. PPGs minimize failure to a partiion and give you visibility on placement.
Info
Use Partition Placement Group if you have large infrastructe platform and provides visibility on placement.
- Spread Placement Group Spread placement groups (SPGs) are designed for a max of seven instances per AZ that need to be separated. Each instance occupies a partition and has an isolated fault domain.
Info
Use Spread Placement Group for maximum availability.
EC2 Billing Models - Spot Instances
Info
Default Billing Model of EC2 is per-second charge for compute instance.
Spot instance allow consumption of spare AWS capacity for a given instance type and size in a specific AZ. Instances are provided for as long as your bid price is above the spot price, and you ony ever pay the spot price. If your bid is exceeded, instances are terminated with a two-minute warning.
Spot fleets are a container for “capacity needs”. You can specify pools of instances of certain types/sizes aiming for a given “capacity”. A minimum percentage of on-demand can be set to ensure the fleet is always active.
Spot instances are perfect for non-critical workloads, burst workloads or consistent non-critical jobs that can tolerate interruptions without impacting functionality. Spot is not suitable for long-running workloads that require stability and cannot tolerate interruptions.
Info
Spot instances are not suitable for long-running workoads that require stability and cannot tolerate interruptions.
Tip
Spot Pricing can save you more than 90% than on-demand application.
EC2 Billing Models - Reserved Instances
Reserved instance lock in a reduced rate for one or three years. Zonal reserved instance include a capacity reservation. Your commitment incurs costs even if instance aren’t launched. Reserved purchases are used for long-running, understood, and consistent workloads.
When to Use Reserved Purchases
- Base / Consistent Load
- Known and Understood Growth
- Critical Systems / Components
When to Use Spot Instances / Fleets
- Burst-y workloads
- Cost-critial, when can cope with interruptions
When to Use On-Demand
- Default or unknown demand
- Anything in between reserved/spot
- Short-term workloads that cannot tolerate interruptions
Dedicated Hosts
EC2 dedicated hosts are a feature of EC2, giving you complete control over physical instance placement and dedicated hardware free from other customer interaction. Dedicated hosts are EC2 hosts for a given typ and size that can be dedicated to you. The number of instances that can run on the host is fixed - depending on the type and size. An on-demand or reserved fee is charged for the dedicated host - there are no charges for instance running on the host. Dedicated hosts are generally used when software is licensed per core/CPU and not compatibile with running within a shared cloud environment.
Info
For dedicated host, you are paying for the hourly charge.