07 - Storage and Content Delivery
S3 Architecture and Features
Permissions
Bucket authorization within S3 is controlled using Identity Policies on AWS identities, as well as Bucket policies in the form of resource policies on the bucket and bucket or object ACLs.
Identity Policies can be applied to roles, groups or users. Identity policies can be used to give permission within the same account.
Bucket Policies
Bucket policies are resource policies that are applied to S3. They can be used to authorize access to a bucket or objects inside a bucket to large numbers of identities. Bucket policies can also apply to anonymous accesses. Bucket policies grant permissions to IAM identities in a different AWS account, known as cross-account access. These permissions can be set instead of using IAM roles.
ACLs are legacy manner to control access to S3 buckets.
Warning
Block public access is a setting applied on top of any existing settings as a protection. It can disallow all public access granted to a bucket and objects using ACLs or bucket policies.
Transferring Data to S3
Uploads to S3 are generally done using the S3 console, CLI or directly using the APIs
Single PUT Upload (Default)
- Limit of 5 GB of Data, can cause performance issues, and if the upload fails the whole upload fails.
- Object is uploaded in a single stream of data
Multi Part Upload
- An object is broken up into parts, each part is 5MB to 5GB
- Multipart upload is faster, and the individual parts can fail and can be retried individually.
- In a S3 multipart upload, an object can be broken up into 10,000 parts.
Note
AWS recommends multipart for anything over 100 MB, but it’s required for anything beyond 5 GB.
S3 Transfer Acceleration enables fast, easy, and secure transfers of files over long distances between your client and an S3 bucket.
Encryption
Data between a client and S3 is encrypted in transit. Encryption at rest can be configured on a per-object basis.
-
Client-Side Encryption - The client/application is responsible for managing both the encryption/decryption process and its keys. This method is genrally only used when strict security complaince is required. It has significant admin and processing overhead.
-
Server-Side Encryption with Customer Managed Keys (SSE-C) - S3 handles the encryption and decryption process. The customer is still responsible for key management, and key must be supplied with each PUT or GET request.
-
Server-Side Encryption with S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3) - Objects are encrypted using AES-256 by S3. The keys are generated by S3. Keys are stored with objects in an encrypted form.
-
Server-Side Encryption with AWS KMS-Managed Keys (SSE-KMS) - Objects are encypted using individual keys generated by KMS. Encrypted keys are stored with the encrypted objects. Decryption of an object needs both S3 and KMS key permission (role seperation).
Note
Object Enryption is done on per-object basis. You can specify default encryption type.
Static Websites and CORS
Amazon S3 buckets can be configured to host websites. Content can be uploaded to the bucket and when enabled, static web hosting will provide a unique endpoint URL that can be accessed by any web browsers. S3 can host many types of content, including:
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Media(Audio, Movies, Images)
S3 can be used to host front-end code for serverless application or an offload location for static content. CloudFront can also be added to improve the speed and efficiency of content delivery for global users or to add SSL for custom domains.
CORS is a security measure allowing a web application running in one domain to reference resources in another.
Object Versioning
By Default Object Versioning is turned off. Once enabled, any operation that would otherwise modify objects generate new versions of that original object. Once a bucket is version-enabled, it can never be fully switched off - only suspended.
With versioning enabled, an AWS account is billed for all versions of all objects. Object deletions by default don’t delete an object - instead, a delete marker is added to indicate the object is deleted.
MFA Delete is a feature designed to prevent accidental deletion of object. Once enabled, a one-time password is required to delete an object version or when changing the version state of a bucket.
Presigned URL
A presigned URL is a temporary URL that allows users to see assigned S3 objects using the creator’s credentials. A presigned URL can be created by an identity in AWS, providing access to an object using the creator’s access permission. When the presigned URL is used, AWS verifies the creator’s access to the object. The URL is encoded with authentication built in and has an expirty time.
Presigned URLs can be used to download or upload objects.
Note
For generating pre-signed URLs, do not generate presigned URLs using Roles and use identities with long term credentials.
S3 Performance and Resilience
Storage Tiers / Classes
All objects within a S3 bucket use a storate class, also known as storage tier. Storage classes influence that cost, durability, availability and “first byte latency” for objects in S3. The class used for an object can be changed manually or using lifecycle policies.
Standard
- Default, all purpose storage or when usage is unknown
- 99.999999999999 (11 nines) durability and four nines availibility
- Replicated in +AZs - no minimum object size or retreival fee
Standard Infrequent Access (Standard - IA)
- Objects where real-time access is required but infrequent
- 99.9% Availability, 3+ AZ replication, cheaper than Standard
- Minimum storage duration of 30-day and 128 KB minimum charge and object retrieval fee
One Zone - IA
- Non-critical and/or reproducible objects (Non Mission Critical)
- 99.5% availability, only 1 AZ, 30 days and 128KB minimum charges
- Cheaper than Standard and Standard IA
Glacier
- Long-term archival storage (warm and cold backups)
- Retrievals could take minutes or hours (faster = higher cost)
- 3+ AZ replication, 90 day and 40KB minimum charge and retrieval
Glacier Deep Archive
- Long-term archival(cold backups) - 180 days and 40KB minimums
- Longer retrievals but cheaper than Glacier - replacement for tape-style storage
Intellgent Tiering
Intellegent-Tiering is a special type of storage class designed for unknown or unpredictable access patterns. It moves objects automatically between two tiers - one designed for frequent access, the others for infrequent.
Lifecycle Rules
Storage classes can be controlled via Lifecycle Rules, which allow for the automated transition of object between storage classess, or in certain cases allow for the expiration of objects that are no longer required.
Info
S3 lifecycle rules can apply to buckets, prefixes, and tags for buckets or objects, along with current or previous versions of an object.
S3 Cross Region Replication
S3 cross-region replication (S3 CRR) is a feature that can be enabled on S3 buckets allowing one-way replication of data from a source bucket to a destination bucket in another region.
By default, replicated objects keep their:
- Storage Class
- Object name(key)
- Owner
- Object permission
S3 CRR requires versioning enabled on both end. Replication requires an IAM role with permission to replicate objects, With the replication configuration, it is possible to override the storage class and object permission as they are written to the destination.
Info
Objects added before the replication configuration added won’t be added as part of the replication process.
- Object ownership and its associated storage tiers can be altered when going to a new region.
- Lifecycle rules do not carry over for S3 CRR
- SSE-C is not supported for CRR
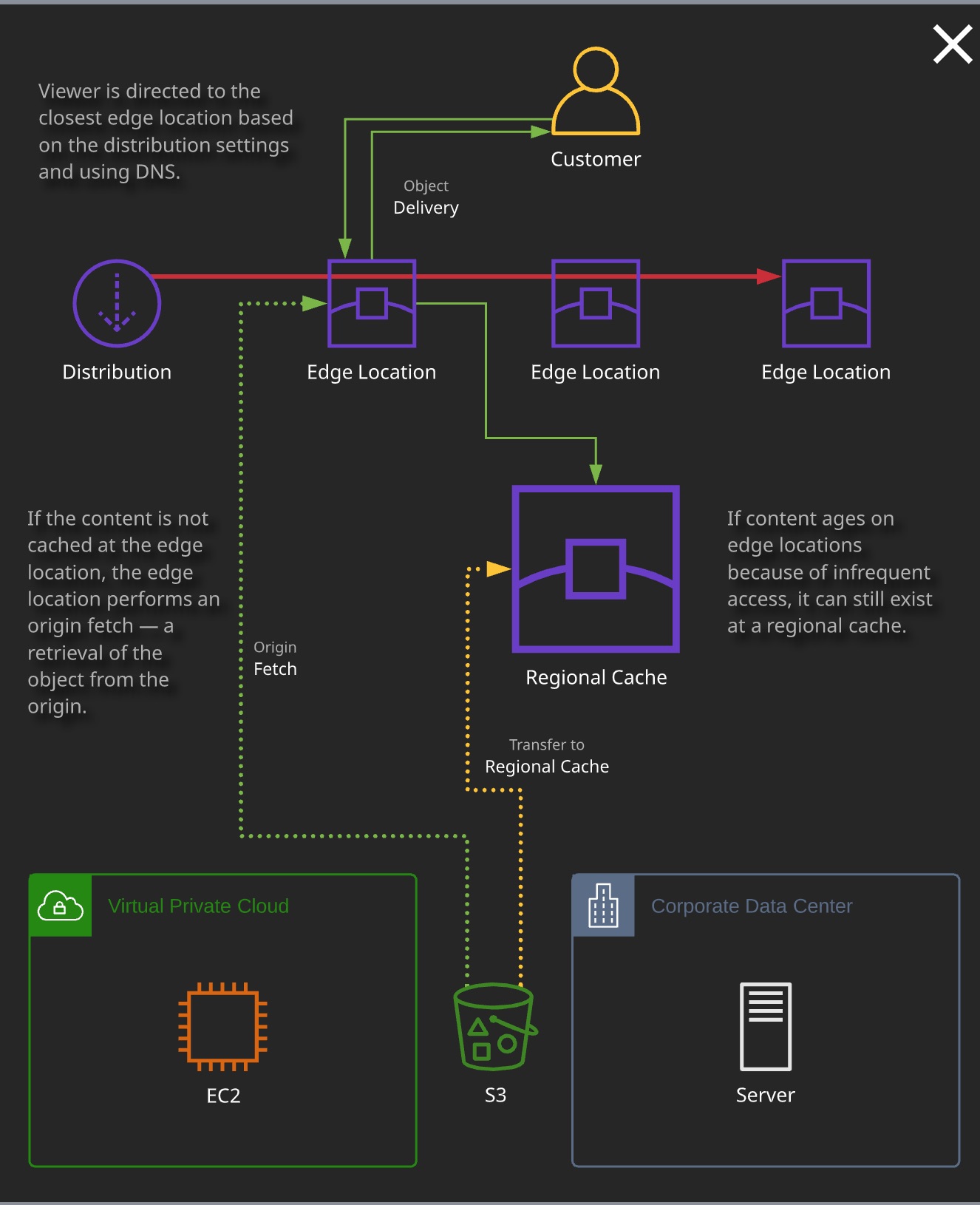
Cloud Front
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Benefits
- Lower Latency
- Higher Transfer Speed
- Reduced Load on Content Server
CloudFront Components
- Origin - The Server or service that hosts your content
- Distribution - The “configuration” entity with CloudFront
- Edge Location - The local infrastructure that hosts caches of your data.
- Regional Edge Caches - Large versions of edge locations.
Origin Access Identity (OAI)
- OAI is a virtual identity associated with Cloud Front Distribution. It only works for S3 Buckets.
- Restrict S3 Bucket access only via Cloud Front
- Why ?
- Performance
- User Experience
Network File System
Amazon EFS
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) provides a simple, scalable, fully managed elastic NFS file system for use with AWS Cloud services, and on-premises resource. File system can be created and mounted on multiple Linux instances at the same time. It is a popular shared storage system that can be natively mounted as a file system within Linux instances.
Amazon EFS offers two storage classes: The Standard storage class, Infrequent Access Storage Class.
Throughput modes
- Bursting Throughput - (Default)
- Provisioned Throughput - Throoughput Mode
Performance Mode
- General Purpose (Default)
- Max I/O (Designed for large number of instances)
# Install Amazon EFS Utils
sudo yum install -y amazon-efs-utils
sudo mkdir /mnt/efs
sudo mount -t efs fs-d358ff50:/ /mnt/efsDesigned for large scale parallel access of data. Shared media, Logging solutions where various clients need to access Shared Data, Amazon EFS is a good use case. BigData Analytics. Amazon EFS is Region Resilient. Security groups are used to control access to NFS mount targets.