06 - Databases
SQL - RDS
RDS is a Database as a Service (DBaaS) product. It can be used to provision a fully functional database without the admin overhead traditionally associated with DB platforms. It can perform at scale, be made publicly accessible, and can be configured for demanding availability and durability scenarios.
RDS supports a number of database engines:
- MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server
- Aurora: An in-house developed engine with substantial features and performance enhancements.
RDS can be deployed in single AZ or Multi-AZ mode (for resilience) and supports the following instance types:
- General purpose (DB.M4 and DB.M5)
- Memory optimized (DB.R4 and DB.R5, and DB.X1e and DB.X1 for Oracle)
Types of storage are supported:
- General Purpose SSD (gp2)
- Provisioned IOPS SSD
RDS instances are charged based on:
- Instance size
- Provisioned storage (Not Used)
- IOPS if using io1
- Data transfer out
- Any backups/snapshots beyond the 100% that is free with each DB instance.
RDS supports encryption with the following limits/restrictions/conditions:
- Encryption can be configured when creating DB instances.
- Encryption can be added by taking a sanpshot, making an encrypted snapshot, and creating a new encrypted instance from that encrypted snapshot.
- Encryption cannot be removed.
Network access to an RDS instance is controlled by a security group (SG) associated with the RDS instance.
Since RDS can only have one master instance at a time, increasing its resources will help with its writing capacity.
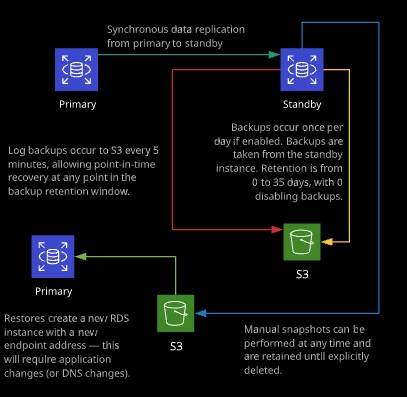
RDS Backups and Restore
RDS is capable of a number of different types of backups. Automated backsups to S3 occur daily and can be retained from 0 to 35 days. (0 means disabled). Manual snapshot are taken manually and exist until deleted, and point-in-time log-based backups are also stored on S3.
- When you restore a snapshot, it will create a brand new instance of RDS with new CNAME.
- When restoring from a backup, a new database will be created, meaning it will not override the existing database.
Info
KMS is a regional service, so if the database is restored to another region, it will require a new master key.
RDS Resilency
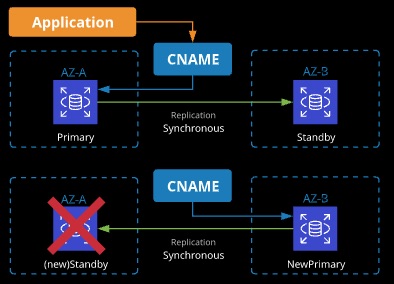
RDS Multi-AZ
- RDS can be provisioned in single or Multi-AZ mode.
- Multi-AZ provisions a primary instance and a standby instance in a different AZ of the same region.
- Only the primary can be accessed using the instance CNAME.
- There is no performance benefit, but it provides a better (Recovery Time Objective) RTO than restoring a snapshot.
With MultiAZ you donot have access to secondary AZ. For RDS only point of contact to the database is via CNAME. For the maintenance, changes happens first on the secondary and then later promoted to primary.
RDS Read Replica
RDS Read Replicas are read-only copies of an RDS instance that can be created in the same region or a different region from the primary instance. Read Replicas can be addressed independently (each having their own DNS name) and used for read workloads, allowing you to scale reads. 5 Read Replicas can be created from a RDS instance, allowing a 5x increase in reads.
- Unlike Multi-AZs, read replicas can be used across regions. They also can be within the same AZ or even across AZs.
- AWS takes care of the networking aspects needed for asynchronous syncing between the primary and secondary regions.
- Unlike Multi-AZ, Read Replicas perform asynchronous replication from the primary to the secondary region.
- The master instance needs to have backups enabled for read replication to occur.
When would you use RDS Read Replica Deployment
- When needing a faster recovery time than restoration from a snapshot
- When most of your DB usage is reading rather than writing, you can scale out your datbase instances for read-only purpose. (Horizontal Scalling)
- Have a Global Resilence
SQL - Aurora
Amazon Aurora is a fully-managed, MySQL-compatible, relational database engine that combines the speed and availability of high-end commercial databases with the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of open source database.
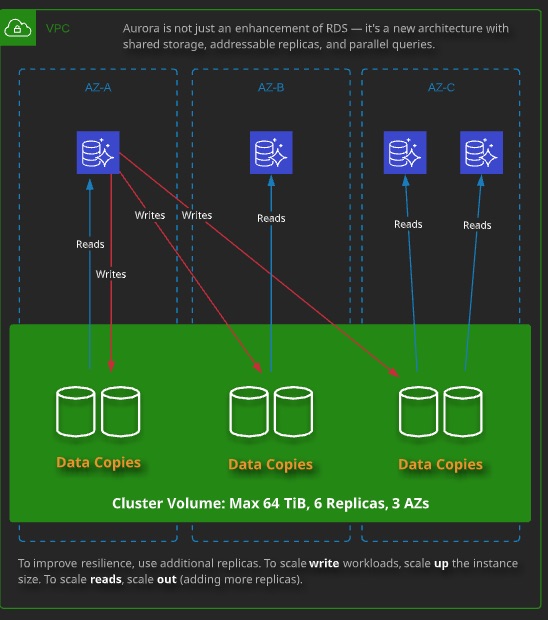
- Aurora uses a base configuration of a cluster - shared storage
- A cluster contains a single primary instance and zero of more replicas.
- All instances (primary and replicas) use the same shared storage - the cluster volumes.
- Aurora cluster volumes automatically scale as the amount of data in your database increases, up to a maximum of 64 tebibytes (TiB)
- AWS Aurora only bills for consumed data, and it’s constantly backed up to S3.
Info
Aurora can have maximum of 15 replicas.
- Automatic Backup
- Snapshot Process
- Backtrack - There is an outage, whenever we do a backtrack. Maximum window of 72 Hours.
- Parallel Queries - The parallel query option allows for optimal performance by allowing query execution across all nodes, at the same time, in a cluster.
Aurora Serverless
Aurora Serverless is a fully managed on-demand, auto-scalling, high-availabile relational database that only charge when it’s in use. Aurora Serverless is based on the same database engine as Aurora, but instead of provisioning certain resouce allocation. Aurora Serverless handles this as a service. You simply specify a minimum and maximum number of Aurora capacity units (ACUs).
Abstracts away the capacity planning for database. You simply pay based on the resource you use (per second). You start with specifying minimum and capacity unit with ACUs.
Common Use case for Aurora Serveless are -
- When an application uses a database and has random surges of traffic
- When you want to remove the complexity of managing database instances
- When you want automatically scaling database instances
- When deploying an application and have unpredictable database usage patterns
- Test environments when you need to Shutdown database when not in use
Notes
- Aurora Serverless exists only in single Availability Zone.
- Aurora Serverless DB clusters can only be accessed from within a VPC.
- With Aurora Serverless, the database endpoint connects to a proxy fleet that routes the workload to a fleet of resources that are automatically scaled.
- Data API allows you to query database using traditional apis. Using Query Editor, a web-based tool you can log into the Aurora Serverless cluster and execute queries.
NoSQL - DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is a key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. It is a NoSQL database service. It’s a regional service, partioned regionally and allows the creation of tables, hence tables names in DynamoDB have to be regionally unique. .
- A Table is a collection of items that share the same partition key (PK) or partition key and sort key(SK) together with other configuration and performance settings.
- An Item is a collection of attributes (upto 400 KB in size) inside a table that shares the same key structure as every other items in the table.
- An attribute is a key and value
- Dynamo DB doesn’t enforce strict schema for items in the collection
- Using Identity Policy, we can provide access to DynamoDB. Unlike S3, you cannot apply resource level policy.
- From resilency perspective, DynamoDB is resilent on regional basis. DynamoDB stores atleast 3 copies of data across different availability zone. DynamoDB handles networking and replication.
user_fav_movies
{
"name": "Bob Smith",
"createdAtTS": 1590268741
"email": "bob.smith@gmail.com",
"fav_movies": [
"Titanic",
"50 First Dates"
]
}
{
"name": "John Doe",
"createdAtTS": 1590268931
"email": "john.doe@gmail.com",
"fav_movies": [
"Beautiful Mind",
"Shutter Island"
]
}Query and Scan Operation
-
Scan - Scan operation has to read every items on the table and apply filter to filter out items that doesn’t match the filter. It is super flexible but it consumers lots of capacity units so it’s so efficent to perform scan query on large tables.
-
Query - Query operation allows to lookup on the table without perform entire table scan, but you need to specify primary key and filter based on sort key. It is more efficent than Scan operation.
-
DynamoDB maintains continuous backups of your table for the last 35 day
-
Manual Backup
-
Encryption comes default with DynamoDB
-
Global Tables - Table needs to be empty and Enabled Streams Enable
-
DynamoDB has full integration with CloudWatch
Performance and Billing
DynamoDB has two read/write capacity modes: Provisioned throughput (default) and on-demand mode. When using on-demand mode, DynamoDB automatically scales to handle performance demands and bills a per-request charge. When using provisioned throughput mode, each table is configured with read capacity units (RCU) and write capacity units (WCU).
DynamoDB is highly resilent and replicates data across multiple AZs in a region. When you receive a HTTP 200, a write has been completed and is durable. This doesn’t mean it’s been written to all AZs - this generally occurs within a second.
An eventually consistent read will request data, preferring speed. It’s possible the data received may not relect a recent write. Eventual consistency is the default for read operations in DDB.
A strong consistency read ensures DynamoDB returns the most up-to-date copy of data - it takes longe rbut is sometimes required for application that require consistency.
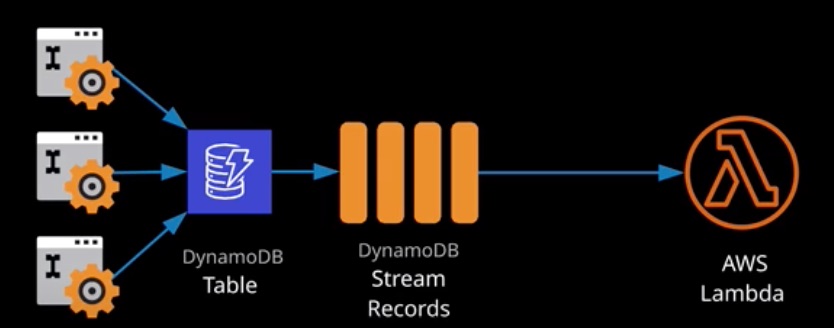
Streams and Triggers
When enabled, streams provide an ordered list of changes that occur to items within a DynamoDB table. A stream is a rolling 24-hour window of changes. Streams are enabled per table and only contain data from the point of being enabled.
Every stream has an ARN that identifies it globally across all tables, accounts, and regions.
Streams can be configured with one of four view types:
- KEYS_ONLY - Whenever an item is added, updated or deleted, the key(s) of that item are added to the stream.
- NEW_IMAGE - The entire item is added to the stream “post-change”
- OLD_IMAGE - The entire item is added to the stream “pre-change”
- NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES - Both the new and old versions of the items are added to the stream.
Streams can be integrated with AWS Lambda, invoking a function whenever items are changed in a DynamoDB table (a DB trigger)
DynamoDB Indexes
Indexes provide an alternative representation of data in a table, which is useful for application with varying query demands. Indexes come in two forms: Local Secondary Indexes (LSI) and Global Secondary Indexes (GSI). Indexes are intracted with as though they are table, but they are just an alternate representaiton of data in an existing table.
Local secondary indexes must be created at the same time as creating a table. They use the same partition key but an altneative sort key. They share the RCU and WCU values for the main table. With using LSI efficient queries can be performed based on alternative sort key. You can create upto 5 LSI per table.
Global secondary indexes can be created at any point after the table is created. They can use different partition and sort keys. They have their own RCU and WCU values. You can create upto 20 GSI per table.
Indexes can have certain projected attributes.
In-Memory Caching
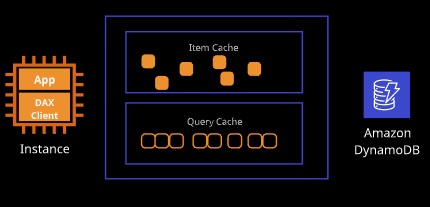
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) is an in-memory cache designed specifically for DynamoDB. Results delivered from the DAX are available in microseconds rather than in the single-digit millisecond available from DynamoDB.
DAX maintains two distinct caches: the item cache and the query cache. The item cache is populated with results from the GetItem and BatchGetItems and has a five minute default TTL. The query cache stores results of Query and Scan operations and caches based on the parameters specified.
Use Case
- Read Intensive Applications
- Applications that are latency sensitive (Real-time bidding, Online Stores)
Elastic Cache
ElasticCache is a managed in-memory data store supporting the Redis or Memcached engines.
ElastiCache is used for two common use cases:
- Offloading database reads by caching responses, improving application speed and reducing costs
- Storing user sessions state, allowing for stateless compute instances (used for fault-tolerant architectures)
Generally, ElastiCache is used with key value databases or to store simple sessions data but it can be used with SQL datbase engines.