07 - Hybrid and Scaling
- Load Balancing and Auto Scalling
- Launch Templates and Configurations
- Auto Scalling Groups
- VPN and Direct Connect
- Snowball and Snowmobile
- Data and DB Migration
- Identity Federation and SSO
Load Balancing and Auto Scalling
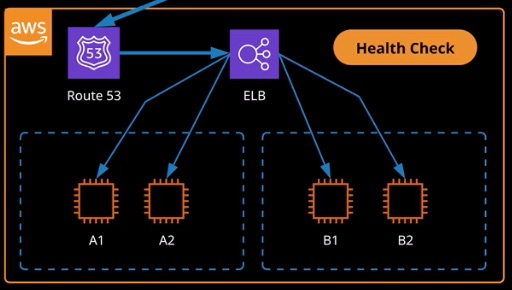
Load balancing is a method used to distribute incoming connections across a group of servers or services. Incoming connections are made to the load balancer, which distributes them to associated services.
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
- ELB is a service that provides a set of highly available and scalable load balancers in one of three versions: Classic (CLB), Application (ALB) and Network (NLB).
- ELBs can be paired with Auto Scaling groups to enhance high availability and fault tolerance - automating scaling / elasticity.
- An elastic load balancer has a DNS record, which allows access to the external side.
- An elastic load balancer can be public facing, meaning it accepts traffic from the public internet or internal, which is only accessible from inside a VPC and is often used betwen application tiers.
- An elastic load balancer accepts traffic via listerers using protocol and ports. It can stirp HTTPS at this point, meaning it handles encryption/decryption, reducing CPU usage on instances.
Classic Load Balancers
- CLB are the oldest type of load balancers and genrally should be avoided for new projects.
- Support L3 and L4 (TCP and SSL) and some HTTP/S features
- It isn’t L7 device, so no real HTTP/S
- One SSL certificate per CLB - can get expensive for complex projects
- Can offload SSL connections - HTTPS to the load balancer and HTTP to the instance (lower CPU and admin overhead on instances)
- Can be associated with Auto Scaling groups
- DNS A Record is used to connect to the CLB
Application Load Balancers
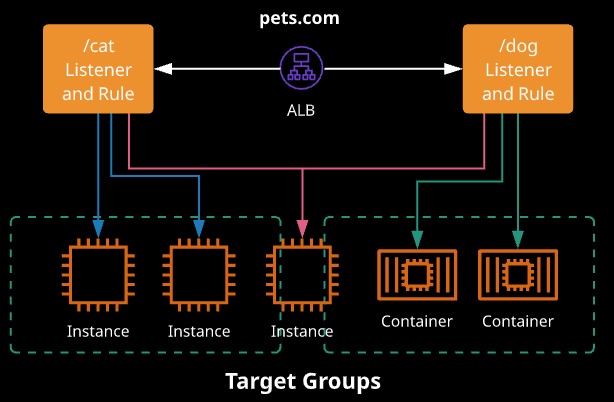
- ALB operates on L7 of the OSI model. They understand HTTP and HTTPS and can load balance based on this protocol layer.
- ALBs are now recommend as the default LB for VPCs. They perform better than CLBs and are most always cheaper.
- Content rules can direct certain traffic to specific target groups.
- Host-based rules: Route traffic based on the host used
- Path-based rules: Route traffic based on URL path
- ALBs support EC2, ECS, EKS, Lambda, HTTPS, HTTP/2 and WebSockets, and they can be integrated with AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Use an ALB if you need to use containers or microservices.
Network Load Balancers
Network Load Balancers (NLB) are the newest type of load balancers and operate at Layer 4 of the OSI network model.
Best load balancing in terms of performance within AWS
Launch Templates and Configurations
Launch templates and launch configuration allow you to configure various configuration attributes that can be used to launch EC2 instances. Typical configuration that can be set include:
- AMI to use for EC2 launch
- Instance type
- Storage
- Key pair
- IAM role
- User data
- Purchase options
- Network configuration
- Security group(s)
Launch template address some of the weaknesses of the legacy launch configurations and add the following features:
- Versioning and inheritance
- Tagging
- More advanced purchasing options
Launch templates should be used over launch configuration where possible. Neither can be edited after creation
Auto Scalling Groups
Auto Scaling groups use launch configuration or launch template and allow automatic scale-out or scale-in based on configurable metrics. Auto Scaling groups are often paired with elastic load balancers.
Metrics such as CPU utilization or network transfer can be used either to scale out or scale in using scaling policies. Scaling can be manual, scheduled, or dynamic. Cooldowns can be defined to ensure rapid in/out events don’t occur.
Scaling
Scaling can be Manual, Scheduled or Dynamic. Scaling policies can be simple, step scaling, or target tracking.
Cooldowns can be defined to ensure rapid in/out events don’t occur.
VPN and Direct Connect
VPN
VPC Virtual Private Network (VPN) provide a software based secure connection between a VPC and on-premise networks.
VPC VPN Components
- A customer gateway (CGW) - configuration for on-premise router
- Virtual Private Gateway attached to VPC
- VPN connection (using one or two IPSec tunnels)
Single Tunnel with Single Customer Gateway
- Simple
Full AWS Resilency with Two Tunnel Endpoint
- Two Tunnels in two different AZs
Full High Available VPN Connection
- Two VPN connections between two different Customer Gateways
- Resilency against Failure of Customer Gateway or VPN
Direct Connect (DX)
A Direct Connect (DX) is a physical connection between your network and AWS either directly via a cross-connect and customer router at a DX location or DX partner.
Virtual Interfaces (VIFs) run on top of a DX. Public VIFs can access AWS public services such as S3 only. Private VIFs are used to connect into VPCs. DX is not highly available or encrypted.
VPN vs Direc Connect or Both
VPN
- Urgent need - can be deployed in minutes
- Cost constrained - cheap and economical
- Low end or consumer hardware - DX requires BGP
- Encryption Required
- Flexible to change locations
- Highly available options available
Direct Connect
- Higher throughput
- Consistent performance (throughput)
- Consistent low latency
- Large amount of data - cheaper than VPN for higher volume
- No contention with existing internet connection
Both
- VPN as a cheap HA option for DX
- VPN as an additional layer of HA
- If some form of connectivity is needed immediately, use VPN before DX connection is live
- Can be used to add encryption over the top of a DX
Snowball and Snowmobile
Used when moving large amount of data quickly in and out of AWS
With any of the snow* devices, you don’t need to worry about writing code or the speed or data allocation of your internet, VPN or DX connection. With snow*, you log a job and receive an empty device or one full of the data requested. You can perform a data copy with your usual tooling and ship the device back.
Snowball
- Can be used for in and out jobs
- Ideal for TB or PB data transfers - 50 TB or 80TB capacity per Snowball
- 1 GBps or 10 GBps using a SFP Data encryption using KMS
- Generally used from 10 TB -> 10 PB
- End-to-end process time is low for the amount of data week(s)
Snowball Edge
- Includes both storage and compute
- Larger capacity
- 10 Gbps
- Compute can be used for local instances or Lambda functionality
- Three versions:
- Edge Storage Optimized: 80TB, 24vCPU, 32 GB RAM
- Edge Compute Optimized: 100TB, 52vCPU, 208 GB RAM
- Edge Compute Optimized with GPU
- Compute can be used for local IoT for data processing prior to ingestion into AWS, and much more
- Used in the same type of situations as Snowballs but when compute is required
Snowmobile
- Portable storage data center within a shipping container on a semi-truck
- Available in certain areas via special order from AWS
- Used when single location 10PB+ is required
- Each Snowmobile can transfer up to 100 PB
- Not economical for sub 10 PB and where multiple locations are required
- Situated on side and connected into your data center for the duration of the transfer
Data and DB Migration
Storage Gateway
Storage Gateway is a hybrid storage service that allows you to migrate data into AWS, extending your on-premises storage capacity using AWS. There are three main types of Storage Gateway: file gateway, volume gateway and tape gateway.
A file gateway supports a file interface into AWS S3 and combines a server and a virtual software appliance. Using File gateway, you can store and retreive objects in Amazon S3 using NFS and SMB.
Volume Gateway proives cloud-backed stoage volumes that you can mount as Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI). The volume gateway is deployed into your on-premises environment as a VM running on VMWare ESXI, KVM or Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor.
A tape gateway provides cloud-backed virtual tape storage. The tape gateway is deployed into your on-premises environment as a VM running on VMware ESXi, KVM or Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor.
Database Migration Service (DMS)
Database Migration Service (DMS) is a service to migrate relational database. It can migrate to and from any location with network connectivity to AWS.
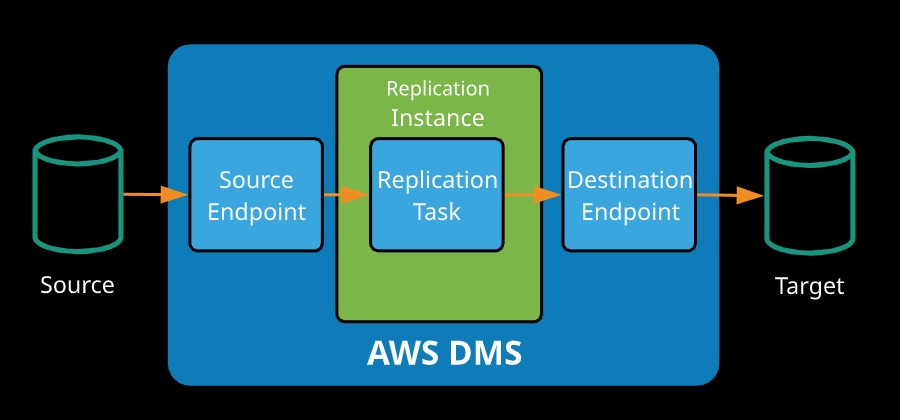
- DMS is compatible with a broad range of DB Sources, including Oracle, MS SQL, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Aurora, and SAP.
- Data can be synced to most of the above engines, as well as Redshift, S# and DynamoDB.
With DMS at high level, you provision a replication instance, define source and destination endpoints that point at source and target databases, and create a replication task. DMS handles the rest, and you can continue using your database while the process runs. DMS is userful in a number of common scenarios:
- Scaling database resources up and down without downtime
- Migrating databases from on-premises to AWS, from AWS to on-premises or to/from other cloud platforms.
- Moving data between different DB engines, including schema conversion.
- Partial / subset data migration
- Migration with little to no admin overhead, as a service
Identity Federation and SSO
Identity Federation (IDF)
Identity Federation (IDF) is an architecture where identities of an external identity provider (IDP) are recognized. Single-sign-on (SSO) is where the credential of an external identity are used to allow access to a local system (e.g. AWS)
Types of IDF inlude:
- Cross-account roles - A remote account (IDP) is allowed to assume a role and access your account’s resources.
- SAML 2.0 IDF - An on-premises or AWS-hosted directory service instance is configured to allow Active Directory users to log in to the AWS console.
- Web Identity Federation - Identity Providers such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook are allowed to assume roles and access resources in your account.
Cognito and the Secure Token Service (STS) are used for IDF. A federated identity is verified using an external IDP and by providing the identity (using a token or assertions of some kind) is allowed to swap that ID for temporary AWS credentitals by assuming a role.
SAML 2.0 Federation
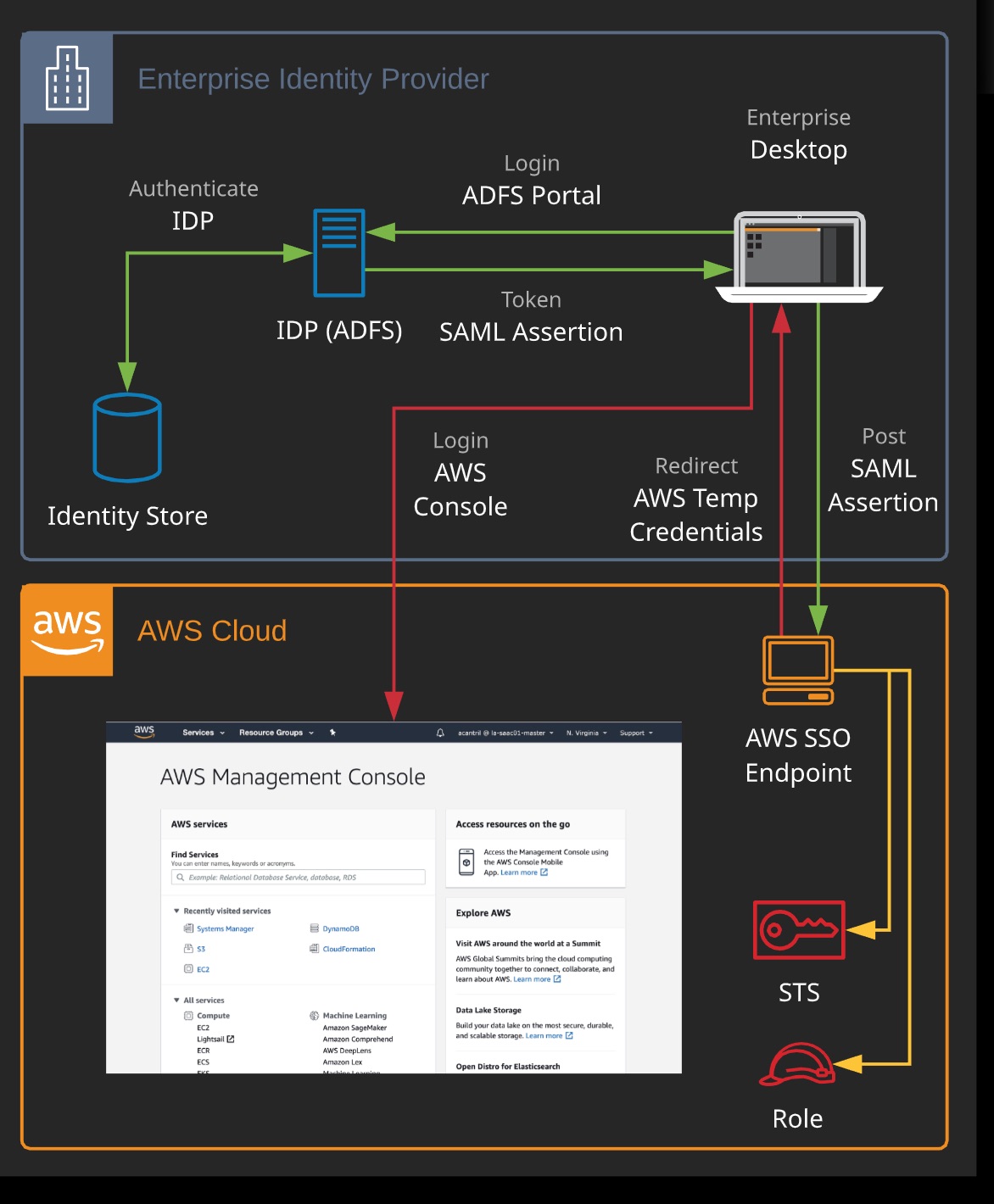
Web Identity Federation
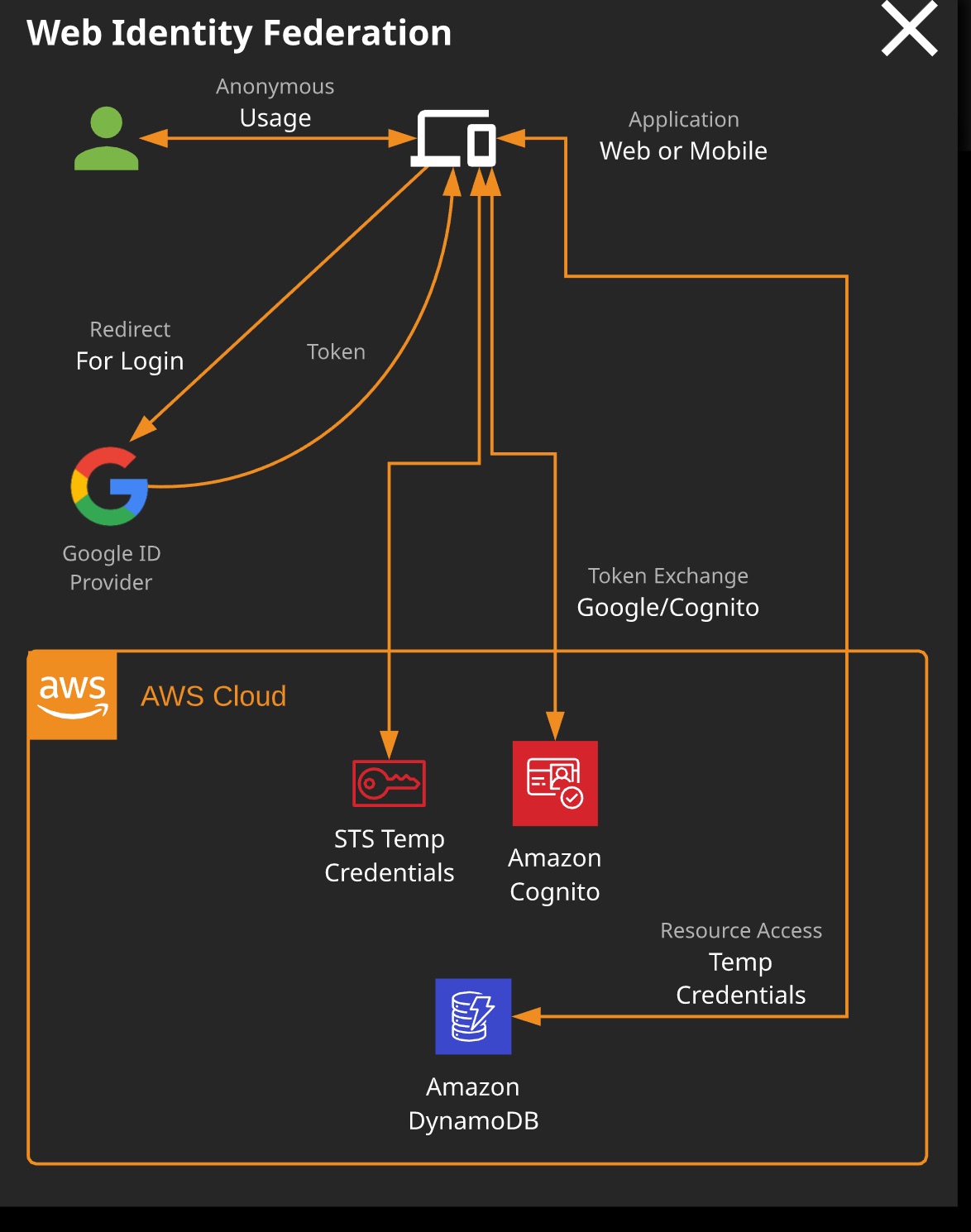
- Users starts with getting redirected to external Identity Provider such as Google, Facebook.
- For valid login, you get a token back
- You use the Token and perform a Token Exchange with Amazon Cognito to get a temporary credentials from STS
- You use the Temporary credentials to perform action on the AWS resource.
When to Use Identity Federation
Enterprise Access to AWS Resources
- Users / staff have an existing pool of identities.
- You need those identities to be used across all enterprise systems, including AWS
- Access to AWS resources using SSO
- Potentially tens of hundreds of thousands of users - more than IAM can handle
- You might have an ID team within your business
Mobile and Web Application
- Mobile or web application requires access to AWS resources
- You need a certain level of guest access
- You don’t want credentials stored within the application
- Could be millions or more users - beyond the capabilities of IAM
- Customers might have multiple third-party logins, but they represent one real person.
Centralized Identity Management (AWS Accounts)
- Tens of hundreds of AWS accounts in an organization.
- Need central store of IDs - either IAM or an existing provider.
- Role switching used from an ID account into member accounts.