09 - Application, Analytics, and Operations
Application Integration
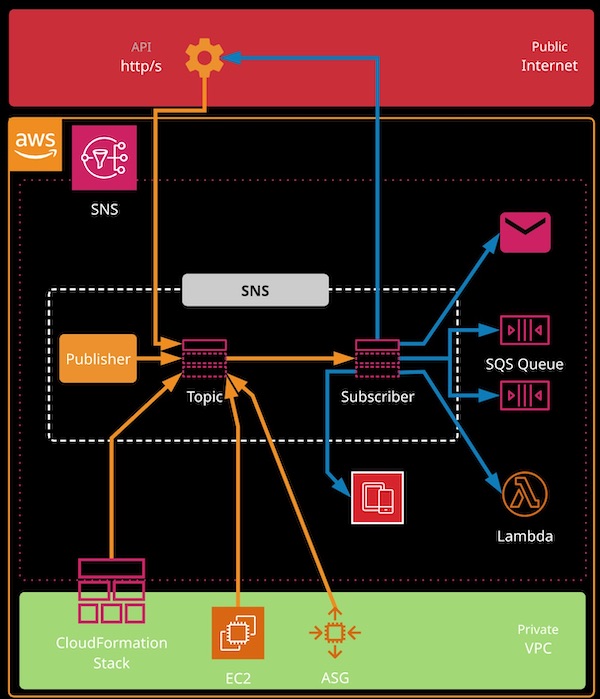
Simple Notification Service (SNS)
- SNS is a Publisher / Subscriber based fully managed Regional Service.
- It is a Public Service.
- SNS coordinates and manages the sending and delivery of messages. Messages sent to a topic are delivered to subscribers
- SNS is integrated with many AWS serviecs and can be used for certain event notifications (e.g. CloudFormation, Stack creation etc)
- Using SNS, CloudWatch can notifiy admins of important alerts
- SNS can be used for mobile push notifications
SNS Components
Topic
- An isolated configuration for SNS, including permissions
- Messages (<= 256 KB) are sent to a topic
- Subscribers to that topic receive messages
Subscribers
- Endpoint that receive message for topic
- HTTP(S)
- SQS (Message can be added to one or more queues)
- Mobile Push Notification
- Lambda Functions
- SMS
Publisher
- An entity that publishes/sends message to queues
- Application
- AWS services, including S3 (S3 events), CloudWatch, CloudFormation etc.
Simple Queue Service (SQS)
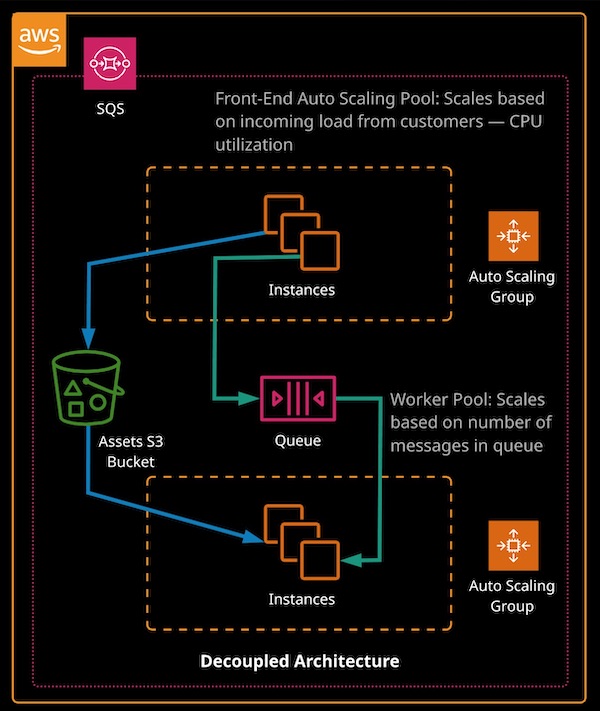
- Simple Queue Service (SQS) provides fully managed, highly available message queues for inter-process /service /service messaging.
- SQS is used mainly to create decoupled architectures.
- Message are added to a queue and retreived via polling.
Polling Types
-
Short Polling: Available messages are returned ASAP - a short poll might return 0 messages. Causes increased number of API calls.
-
Long polling - Waits for message for a given WaitTimeSeconds (More Efficient)
-
Each SQS message can contain upto 256KB of data but can link data stored in S3 for any larger payloads.
-
When a message is polled, it is hidden in the queue. It can be deleted when processing is completed - otherwise, after a VisibilityTimeout period, it will return to the queue.
-
Lambda functions can be invoked based on message on a queue offering better scalling and faster response than Auto Scalling groups for any messages that can be processed quickly.
There are two types of queues: Standard Queues and FIFO queues.
- Standard queues are distributed and scalable to nearly unlimited message volume. The order is not guarantted, best-effort only, and messages are gurantted to be delivered at least once but sometimes more than once.
- FIFO queues ensure first-in,first-out delivery. Messages are delivered once only - duplicates do not occur. The throughput is limited to ~ 3,000 messages per second with batching or ~300 without by default.
## Get Queue Attributes
aws sqs get-queue-attributes --queue-url https://URL --attribute-names All
## Send Message
aws sqs send-message --queue-url https://URL --message-body "INSERTMESSAGE"
## Receive Message
aws sqs receive-message --queue-url https://URL
## Delete Message
aws sqs delete-message --queue-url https://URL --receipt-handle "INSERTHANDLE"
## Receive Message (Long Poll)
aws sqs receive-message --wait-time-seconds 10 --max-number-of-messages 10 --queue-url https://URL
aws sqs --region us-east-1 receive-message --wait-time-seconds 10 --max-number-of-messages 10 --queue-url https://URL
Elastic Transcoder
Elastic Transcoder is an AWS service that allows you to convert media file from an input format to one or more output formats. It’s delivered as a service, and you are billed a per-minute charge while using the service.
A pipeline is a queue for jobs. It stores source and destination settings, notification, security and other high settings. Jobs are processed in the order they are added as resources allow. Pipelines can send notifications as jobs progress through various sates. These might notify an administrator or initiate further even-driven processing.
Analytics
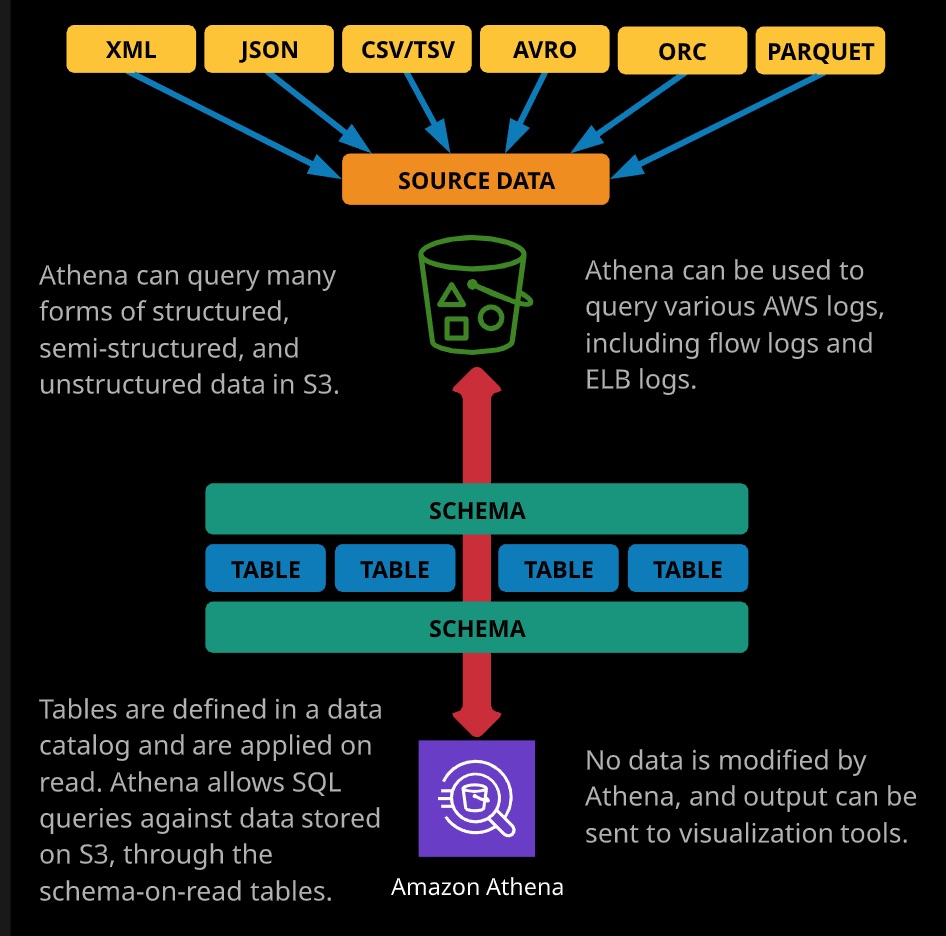
Athena
Amazon Athena is an interactive query servie that utilizes Schema-On-Read, allowing you to run ad-hoc SQL like queries on data from a range of sources. Results are returned in seconds, and you are billed only for the compute time used and any existing storage costs.
Athena can query many forms of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in S3.
Athena is used to query large dataset stored in S3 with in-frequent access pattern. You are charged for compute time only. You don’t need to maintain separate dataset for Athena, it can directly access S3 bucket.
Elastic MapReduce (EMR)
Amazon Elastic MapReduce (EMR) is a tool for large-scale parallel processing of big data and other large data workloads. It’s based on the Apache Hadoop framework and is delivered as a managed cluster using EC2 instances. EMR is used for huge-scale log analysis, indexing, machine learning, financial analysis, simulations, bioinformatics and many other large-scale applications.
EMR cluster have zero or more core nodes, which are managed by the master node. They run tasks and manage data for HDFS.
Data can be input from and output to S3. Intermediate data can be stored using HDFS in the cluster or EMRFS using S3.
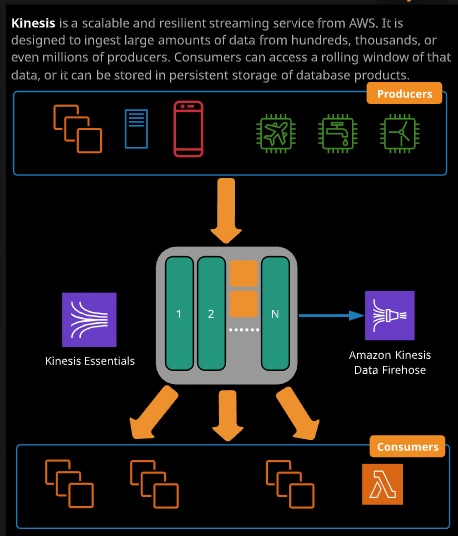
Kinesis and Firehose
Kinesis is a scalable and resilent streaming service from AWS. It is designed to ingest large amounts of data from hundreds, thousands, or even millions of producers. Consumers can access a rolling window of that data, or it can be stored in persistent storage of database products.
Kinesis Stream
A Kinesis stream can be used to collect, process, and analyze a large amount of incoming data. A stream is a public service accessible from inside VPCs or from the public internet by an unlimited number of producers.
Kinesis streams include storage for all incoming data within a 24 hour default window, which can be increased to seven days for an additional charge. Data records are added by producers and read by consumers.
Kinesis Shard
Kinesis shards are added to streams to allow them to scale. A stream starts with at least one shard, which allows 1 MB of ingestion and 2MB of consumption. Shards can be added or removed from streams.
Kinesis Data Record
The basis entity written to and read from Kinesis stream, a data record can be upto 1 MB in size.
You would use Kinesis rather than SQS when you need many producers and many consumers as well as a rolling window of data. SQS is a queue. Kinesis allows lots of independent consumers reading the same data window.
SQS is designed as a Queing Solution to decouple systems whereas Kinesis is designed as more of Publish Subscribe model where message from a producer is consumed by multiple consumers.
Kinesis Firehose
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose is the easiest way to reliably load streaming data into data lakes, data stores and analytics tools. It can capture, transform, and load streaming data into Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, Amazon Elasticsearch Service, and Splunk, enabling near real-time analytics with existing business intelligence tools and dashboards you’re already using today.
Redshift
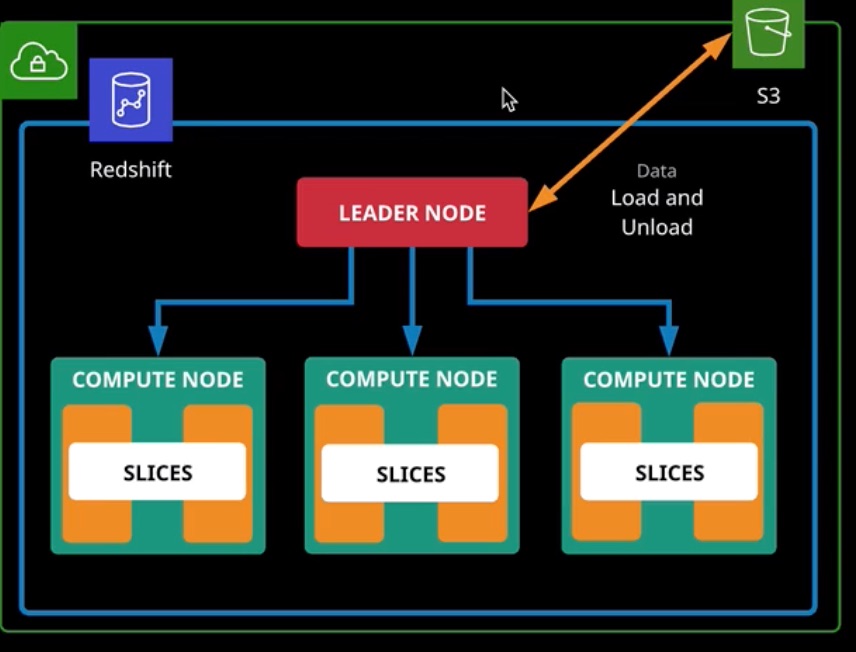
Redshift is a petabyte-scale data warehousing solution. It’s a column-based database designed for analytical workloads. Generally, a relational store like RDS would be used for OLTP workloads (e.g queries, inserts, updates, and deletes), and Redshift would be used for OLAP (e.g. retrieval and analytics). Multiple databases become source data to be injected into a data warehouse solutions such as Redshift.
Data can be loaded from S3 and unloaded to S3. Additionally, backups can be performed to S3, and various AWS services such as Kinesis can inject data into Redshift.
Logging and Monitoring
CloudWatch
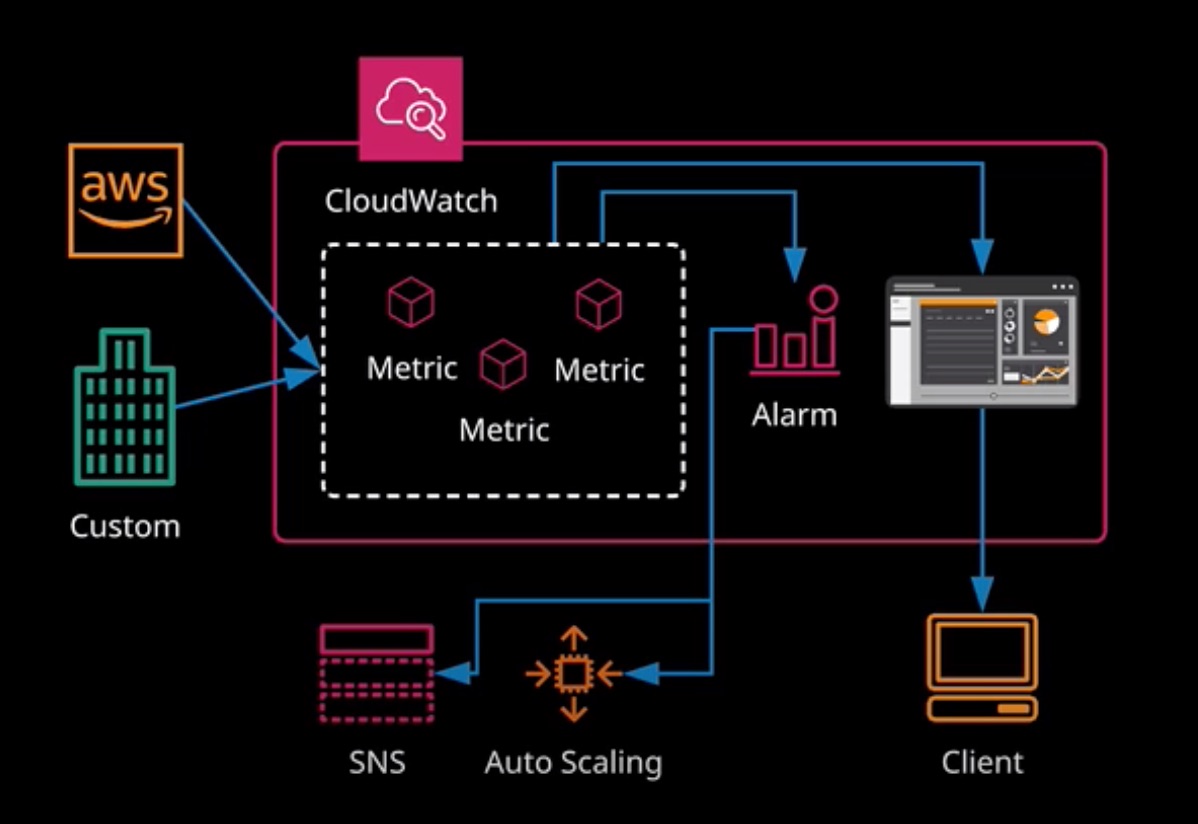
CloudWatch is a service that provides near real-time monitoring of AWS products. In essence, it’s a metrics repository. You can import customer metric data in real-time from some AWS services and on-premises platforms.
Data retention is based on granuality:
- One-hour metrics are retained for 455 days
- Five-minute metrics for 63 days
- One-minute metrics for 15 days
Metrics can be configured with Alarms that can take actions, and data can be presented as a dashboard.
CloudWatch Metrics and Alarms
A CloudWatch metric is a set of data points over time. An example is CPU utilization of an EC2 instance. Alarm can be created on metrics, thaking an action if the alarm is triggered.
Alarms have a number of key components:
- Metric - The data point over time being measured
- Threshold - Threshold value to trigger an alarm
- Period - Time duration for the metric to beyond the Threshold
- Action - What to do when an alarm is triggered.
You can configure Dynamic Alarm so that it can also use Anomalyn detection and trigger an Alarm
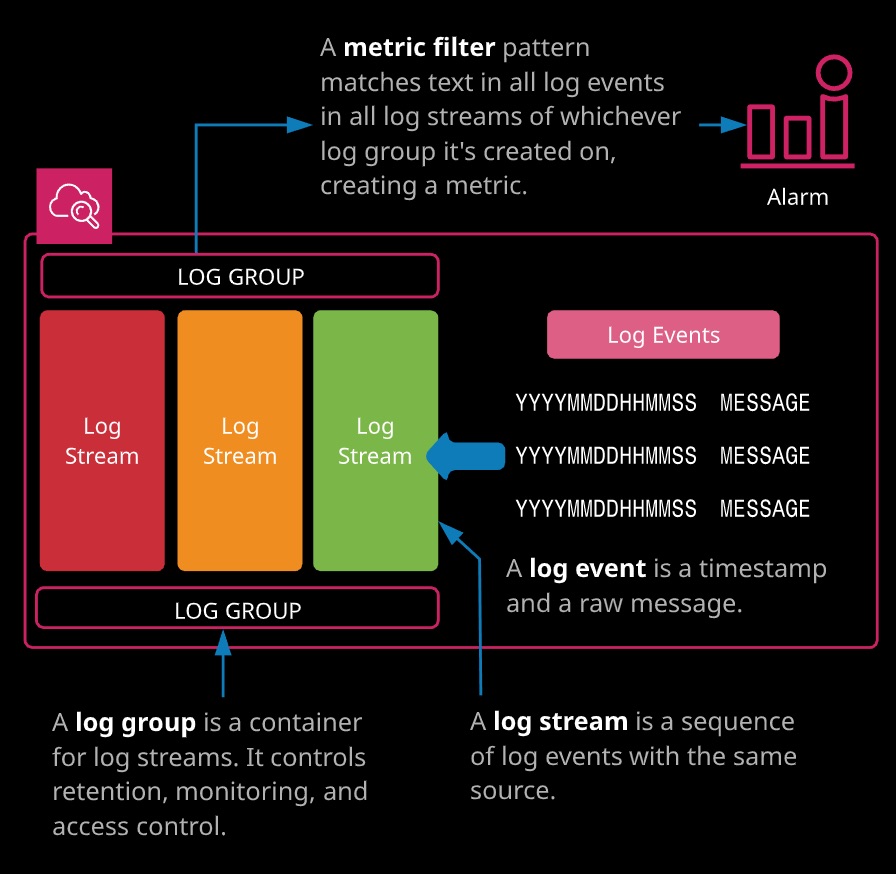
CloudWatch Logs
CloudWatch Logs provides functionality to store, monitor, and access logs from EC2, on-premises servers, Lambda, CloudTrail, Route 53, VPC Flow Logs, customer applications, and much more. Metric filters can be used to analyze logs and create metrics.
- Log Groups - Container for Log Streams.
- Log Streams - A Log Stream is a sequence of log events within the same source.
- Log Events - A Log Event is a timestamp and a raw message.
You can set expiration date for the Log Groups
Cloud Watch Log Metric Filer is creaetd on a Log Group with a pattern match and Alarm can also be created
CloudTrail
CloudTrail is a governance, compliance, risk management and auditing service that records account activity within an AWS account. Any actions taken by users, roles, or AWS services are recorded to the service. Activity is recorded as a CloudTrail event, and by default you can view 90 days via event history. Trails can be created, giving more control over logging and allowing events to be stored in S3 and CloudWatch Logs.
Events can be management events that log control plane events (e.g, user login, configuring security, and adjusting security groups) or data events (eg, Object-level events in S3 or funciton-level events in Lambda).
Cloud Trail service is not real-time and it is delivered in batches.
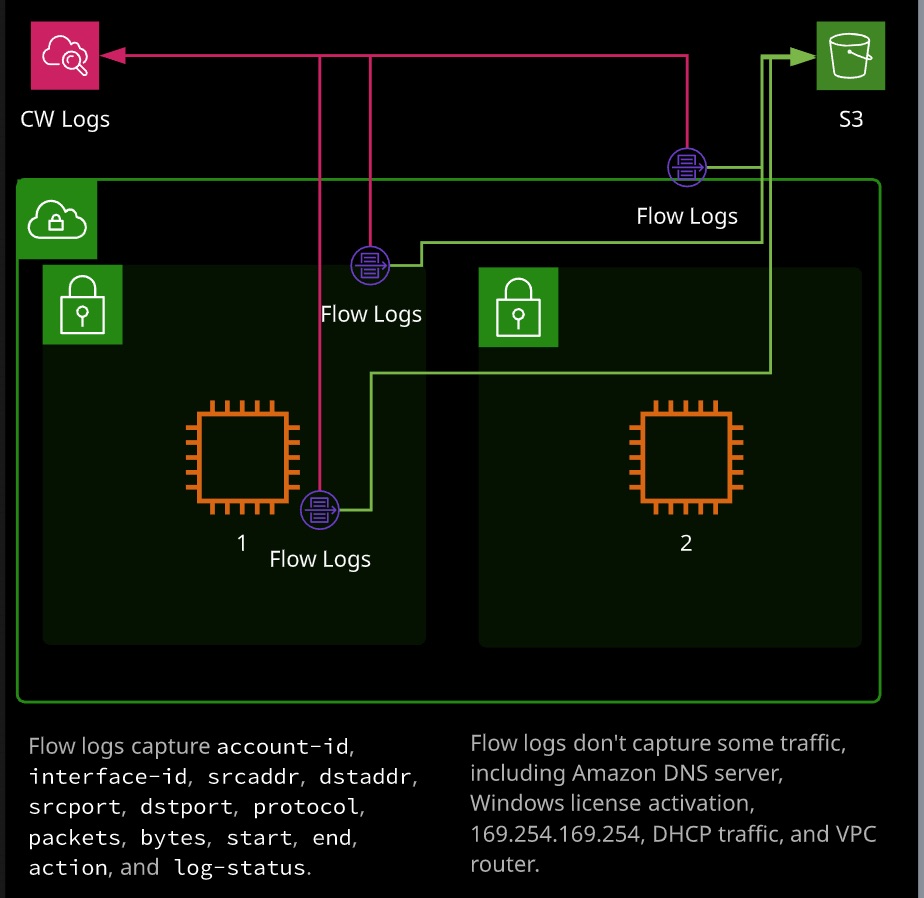
VPC Flow Logs
VPC Flow Logs allows you to capture metadaa about the traffic flowing in and ou of networking inerfaces within a VPC. Flow logs can be placed on a specific network interface, a subnet or an entire VPC and will capture metadata from the capture point and anything within it. Flow logs aren’t real-time and don’t capture the actutal traffic - only metadata on the traffic.
VPC Flow Logs is not real ttime and it only capttures only certain metadata information. Flow Logs don’t capture all traffic logs.
Operations
CloudWatch Events
CloudWatch Eventts has a near real-time visibility of changes that happen within an AWS account. Using rules, you can match against certain events within an account and delivery those events to a number of supported targets.
Within rules, many AWS services are natively supported as event sources and delivery the events directly. For others, CloudWatch allows event pattern matching against CloudTrail events. Additional rules support scheduled events as sources, allowing cron-style function for periodically passing events to targets.
Some examples of event targets include:
- EC2 instances
- Lambda functions
- Step Functions state machines
- SNS topics
- SQS Queues
You can use CloudWatch Events (CRON Style Rule) to stop EC2 Functions.
KMS
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) provides regional, secure key management and encryption and decryption services. KMS is FIPS 140-2 level 2 validated and certain aspects support level 3. Everything in KMS is regional, KMS can use CloudHSM via Custom Key Stores.
KMS manages customer master keys (CMK), which are created in a region and never leave the region or KMS. They can encrypt or decrypt data upto 4KM. CMK’s have key policies and can be used to create other keys. There are three types of CMK
-
AWS Managed CMK: Used by default if you pick encryption within most AWS services and formatted as aws/service-name. Only the service they belong to can use them directly.
-
Customer Managed CMK: Certain services allow you to pick a CMK you manage. Customer managed CMKs allow key rotation configuration, and they can be controlled via key policies and enabled/disabled.
-
AWS Owned CMK: Keys used by AWS on a shared basis across many accounts - you normally don’t see these.
-
KMS can encrypt upto 4KB with a CMK - you supply the data and specify the key to use.
-
It can decrypt data up to 4KB - you provide the ciphertext, and it returns the plaintext
-
You can also re-encrypt up to 4KB - you supply the ciphertext, the new key to use, and you are returned new ciphertext.
# Create Customer Managed Key
aws kms create-key --description "LA KMS DEMO CMK"
# Create Alias for KeyID
aws kms create-alias --target-key-id XXX --alias-name "alias/lakmsdemo" --region us-east-1
# Encrypt a file with CMK
echo "this is a secret message" > topsecret.txt
aws kms encrypt --key-id KEYID --plaintext file://topsecret.txt --output text --query CiphertextBlob
aws kms encrypt --key-id KEYID --plaintext file://topsecret.txt --output text --query CiphertextBlob | base64 --decode > topsecret.encrypted
# Decrypt a Cipher Text
aws kms decrypt --ciphertext-blob fileb://topsecret.encrypted --output text --query Plaintext | base64 --decode
aws kms generate-data-key --key-id KEYID --key-spec AES_256 --region us-east-1
KMS can generate a data encryption key (DEK) using a CMK. You or a service can use a DEK to encrypt or decrypt data of any size. KMS supplies a plaintext version and an encrypted version
# Generate Data Key
aws kms generate-data-key --key-id KEYID --key-spec AES_256
Deployment
Elastic Beanstalk
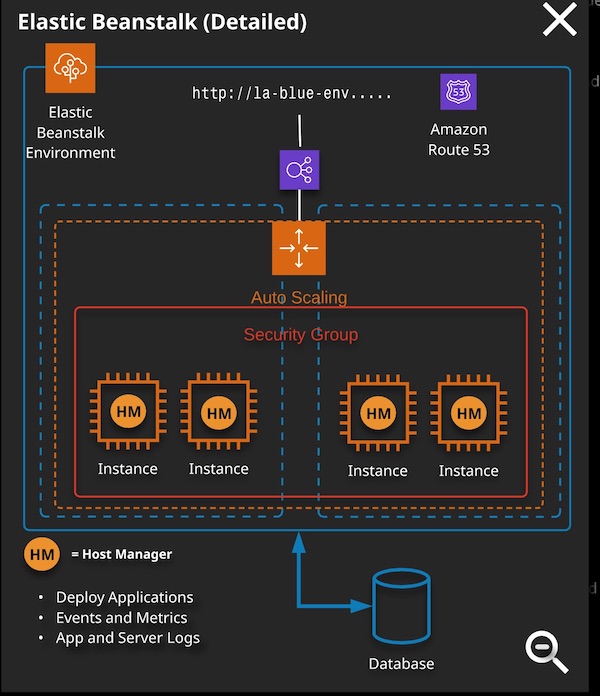
Elastic Beanstalk (EB) is a Platform as a Service product. It allows you to deploy code and, with very little effort or modification, the service will provision the infrastructure on your behalf.
Elastic Beanstalk handles provisioning, monitoring, Auto Scalling, load balancing, and software updating for you - you just worry about the cost.
If you need to provision an environment for an application with little admin overhead and if you use one of the supported languages and can see EB-specific config.
Donot use Elastic Beanstalk if you want low-level infrastructure control.
Deployment Options
- All at Once - An updated application version is deployed to all instances. Quick and simple but not recommended for production deployments.
- Rolling Deployment - Splits instances into batches and deploys one batch at a time
- Rolling with Additional Batch - Similar to Rolling Deployment, but provisions a new batch, deploying and testing before removing the old batch
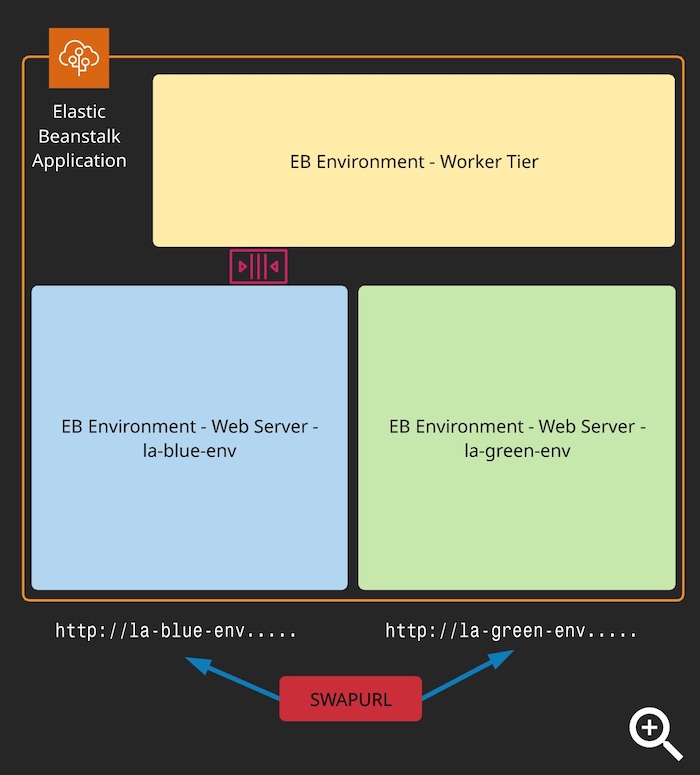
- Blue/Green - Maintains two environments, deploy, and swap CNAME.
OpsWorks
- OpsWork is an implementation of the Chef configuration management and deployment platform.
- OpsWorks move away from the low-level configurability of CloudFormation but not as far as Elastic Beanstalk
- OpsWork lets you create a stack of resources with layers and manage resources as a unit.
OpsWorks Components
- Stacks
- A unit of managed infrastructure
- Can use stacks per application or per platform
- Could use stacks for development, staging, or production environments
- Layers
- Comparable to application tiers within a stack
- e.g, Database Layer, Application Layer, Proxy Layer
- Receipes are generally associated with layers and configuration what to install on instances in that layer
- Instances
- Instances are EC2 instances associated with a layer
- Configured as 24/7, load based, or time based
- Apps
- Apps are deployed to layers from a source code repo or S3
- Actual deployment happens using receipes on layers
- Recipes
- Setup - Executed on an instance when first provisioned
- Configure - Executed on all instances when instances are added or removed
- Deploy and UnDeploy - Executed when apps are added or removed
- Shutdown - Executed when an instance is shut down but before it’s stoppepd