PUT /pages DELETE /pages
PUT /products { "settings": { "number_of_shards": 2, "number_of_replicas": 2 } }
POST /products/_doc { "name": "Cell Phone", "price": 100, "inStock": 10 }
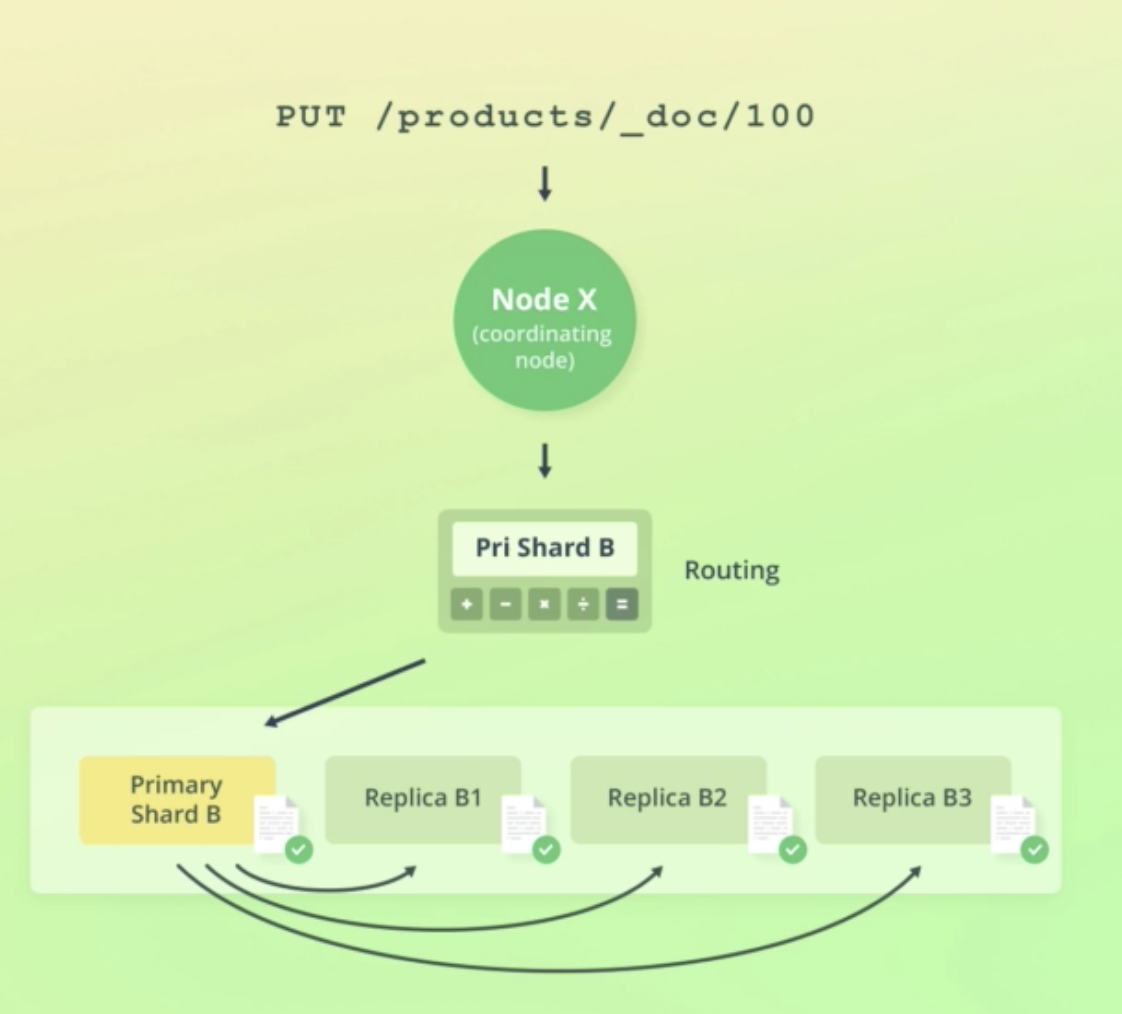
PUT /products/_doc/100 { "name": "Toaster", "price": 20, "inStock": 100 }
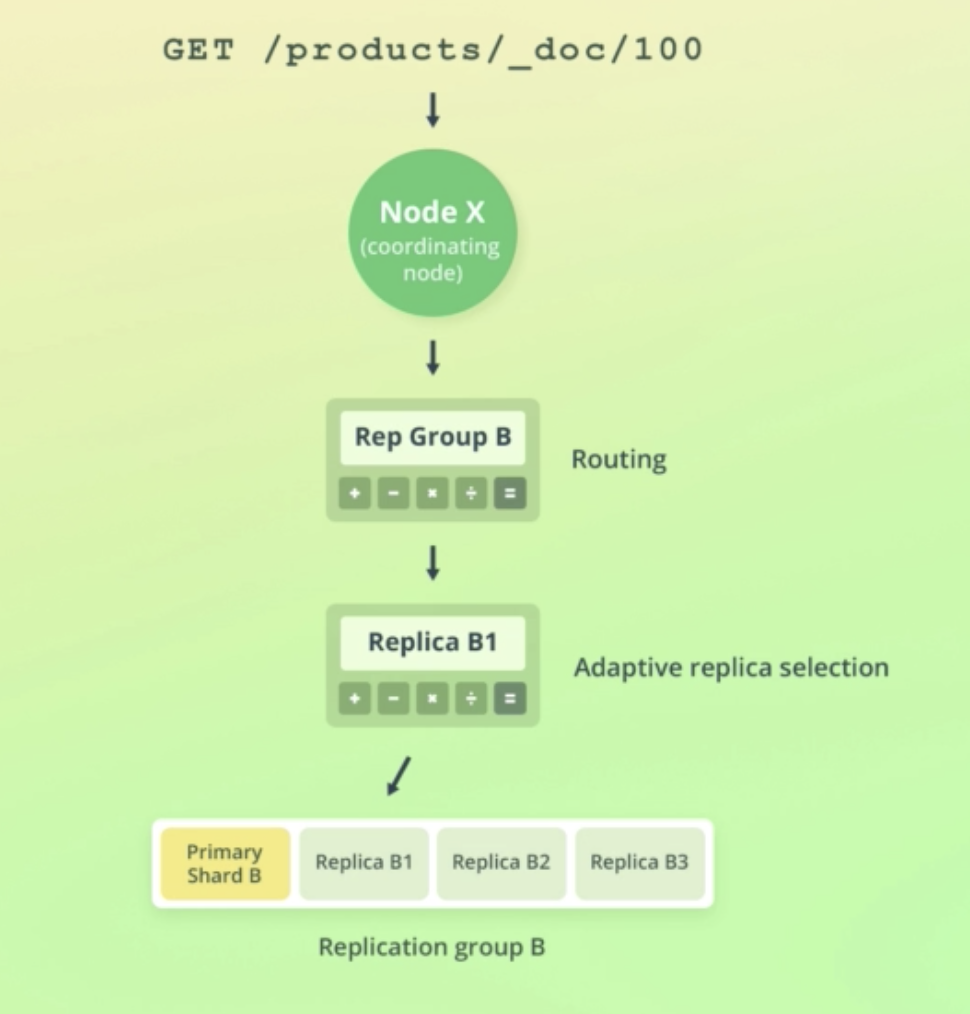
GET /products/_doc/100
POST /products/_update/100 { "doc": { "inStock": 3 } }
POST /products/_update/100 { "doc": { "isAvailable": "true" } }
#######################
#######################
POST /products/_update/100 { "script":{ "source": "ctx._source.inStock++" } }
POST /products/_update/100 { "script":{ "source": "ctx._source.inStock=100" } }
GET /products/_doc/100
#######################
#######################
POST /products/_update/101 { "script":{ "source": "ctx._source.inStock++" }, "upsert": { "name": "Blender", "price": 399, "inStock": 5 } }
GET /products/_doc/101
#######################
#######################
GET /products/_doc/100
PUT /products/_doc/100 { "name": "Toaster", "price": 20, "inStock": 100 }
#######################
#######################
DELETE /products/_doc/100
#######################
#######################
POST /products/_update_by_query {
"script": { "source": "ctx._source.inStock--" }, "query": { "match_all": {} } }
GET /products/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} } }
#######################
#######################
POST /products/_delete_by_query { "query": { "match_all": {} } }
GET /products/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} } }
#######################
POST /_bulk { "index": { "_index": "products", "_id": 200 } } { "name": "Espresso Machine", "price": 199, "inStock": 5} { "create": { "_index": "products", "_id": 201 } } { "name": "Milk", "price": 29, "inStock": 20}
POST /_bulk { "update": { "_index": "products", "_id": 201 } } { "doc": { "price": 10 } } { "delete": { "_index": "products", "_id": 200 } }
GET /products/_search { "query": {"match_all": {}} }
#######################
#######################
GET /_cluster/health
GET /_cat/nodes?v
GET /_cat/indices?v
GET /_cat/shards?v